By: Team W16-4 Since: Aug 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Patient Record Management
- 3.2. Medicine Records System
- 3.3. Queue Management
- 3.3.1. Registering a patient to Waiting Queue:
register - 3.3.2. Listing all patients in Waiting Queue:
queue - 3.3.3. Removing a patient from Waiting Queue:
remove - 3.3.4. Inserting a patient to Waiting Queue:
insert - 3.3.5. Serving the first patient in Waiting queue:
serve - 3.3.6. Adding document contents to Current Patient:
adddocument - 3.3.7. Displaying document contents for Current Patient:
displaydocuments - 3.3.8. Dispensing medicine to Current Patient:
dispensemedicine - 3.3.9. Finishing service of the Current Patient:
finish - 3.3.10. Removing patient from Served Patient Queue:
payment
- 3.3.1. Registering a patient to Waiting Queue:
- 3.4. Document Generation
- 3.5. Miscellaneous
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command Summary
1. Introduction
Ding Dong! Welcome to CLInic!
CLInic is a desktop application designed to streamline and expedite operations in clinics. Regardless of whether you are a doctor or a receptionist at a clinic, merely having an average to high typing speed is the only pre-requisite required to reap its numerous benefits, which includes:
-
Easy management of large databases of patient and medicine information
-
Efficient generation of official documents including receipts and medical certificates
-
Ease of use through helpful graphical displays of obscure technical information
-
User friendly commands that make complicated tasks intuitive
-
Packaged with an elegant queue system that displays the real-time states of the separate queues in the clinic for staff and patients to see
If you wish for a clinic management application that can radically enhance your productivity, then look no further
than CLInic! CLInic will take care of the nitty-gritty complexities of your workflow, allowing you to
focus instead on what truly matters to you as a health care professional: providing quality healthcare services efficiently.
You will have all the tools needed for running a world-class clinic at your fingertips (literally!).
Interested? Continue scrolling to hop onboard with us and get started!
2. Quick Start
Follow the steps below to get started with CLInic.
-
Check you have Java version
9or later installed in your computer. -
Download the latest
CLInic.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your CLInic application.
-
Double-click the file to start the application. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
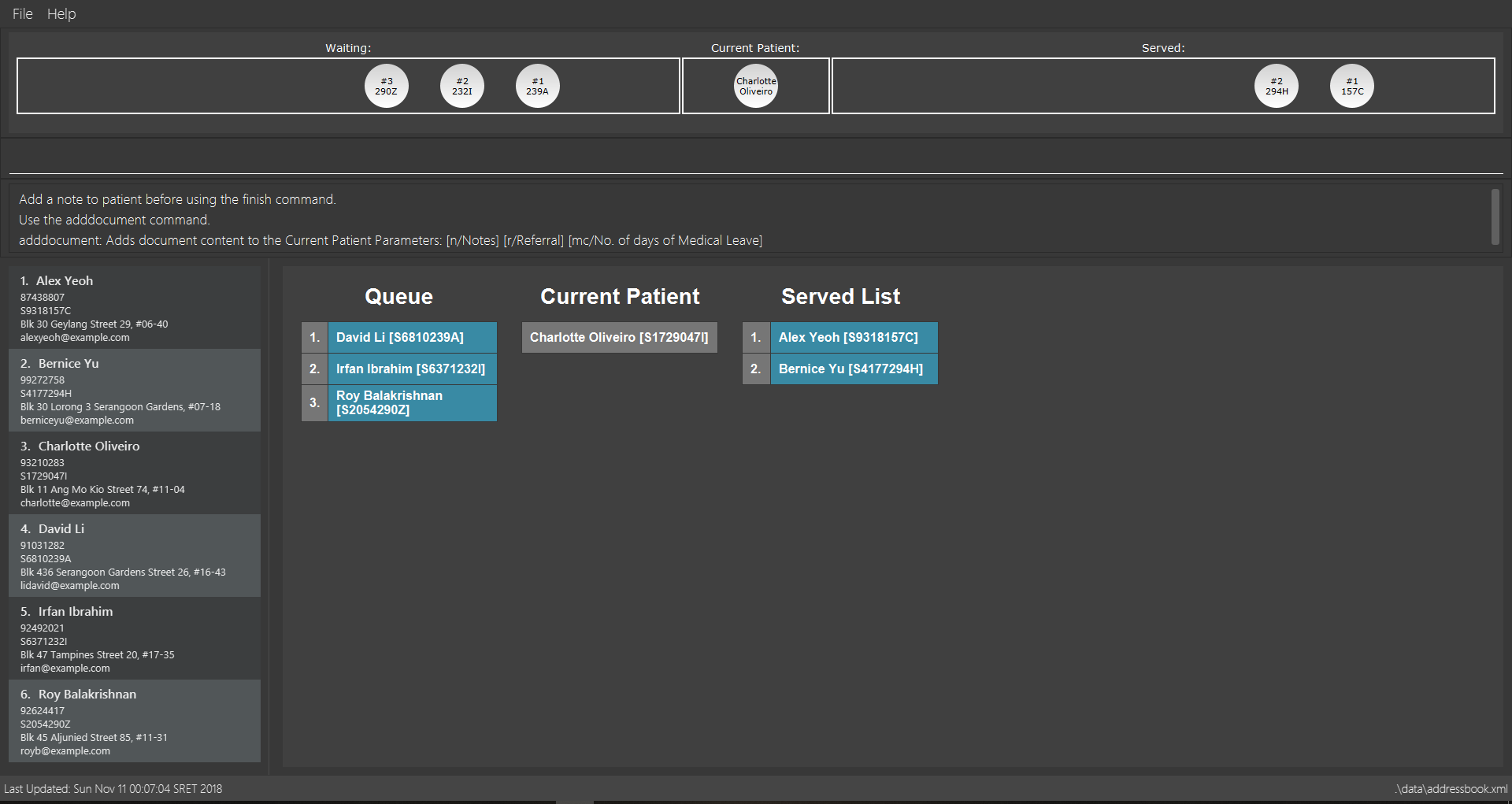 Figure 1. CLInic’s UI
Figure 1. CLInic’s UI -
Type a command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
list: shows a list all patients in the database. -
addn/John Doe ic/S1234567X p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John Street, Block 123, #01-01: adds a patient namedJohn Doeto the database, along with his personal details (more details in Section 5.1, “Patient”). -
delete3: deletes the 3rd patient shown in the current list. -
exit: exits the application.
-
-
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for the details of each command.
3. Features
Command Formats
In this user guide, you will find information about how commands are to be used explained in the form of command formats. These command formats will tell you what the COMMAND_WORD for the command is.
|
3.1. Patient Record Management
3.1.1. Adding a patient: add
Did someone just walk in, wanting to see the doctor?
Add him to CLInic’s patient database using the add command!
Alias: a
Format: add n/NAME ic/IC_NUMBER p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
|
Pro tip(s):
|
|
Important:
Omission of any mandatory parameters will result in the failure of adding the patient to the database.
|
Upon successful execution, you should see the patient with his details added to the patient list on the left.
Examples:
-
add n/Clinton Law ic/S9638902L p/97947435 e/clinton@cs2103t.com a/Tembusu College
Adds a patient namedClinton Law, with IC numberS9638902L, phone number97947435, emailclinton@cs2103t.comand address ofTembusu Collegeto CLInic’s patient database, as shown below.
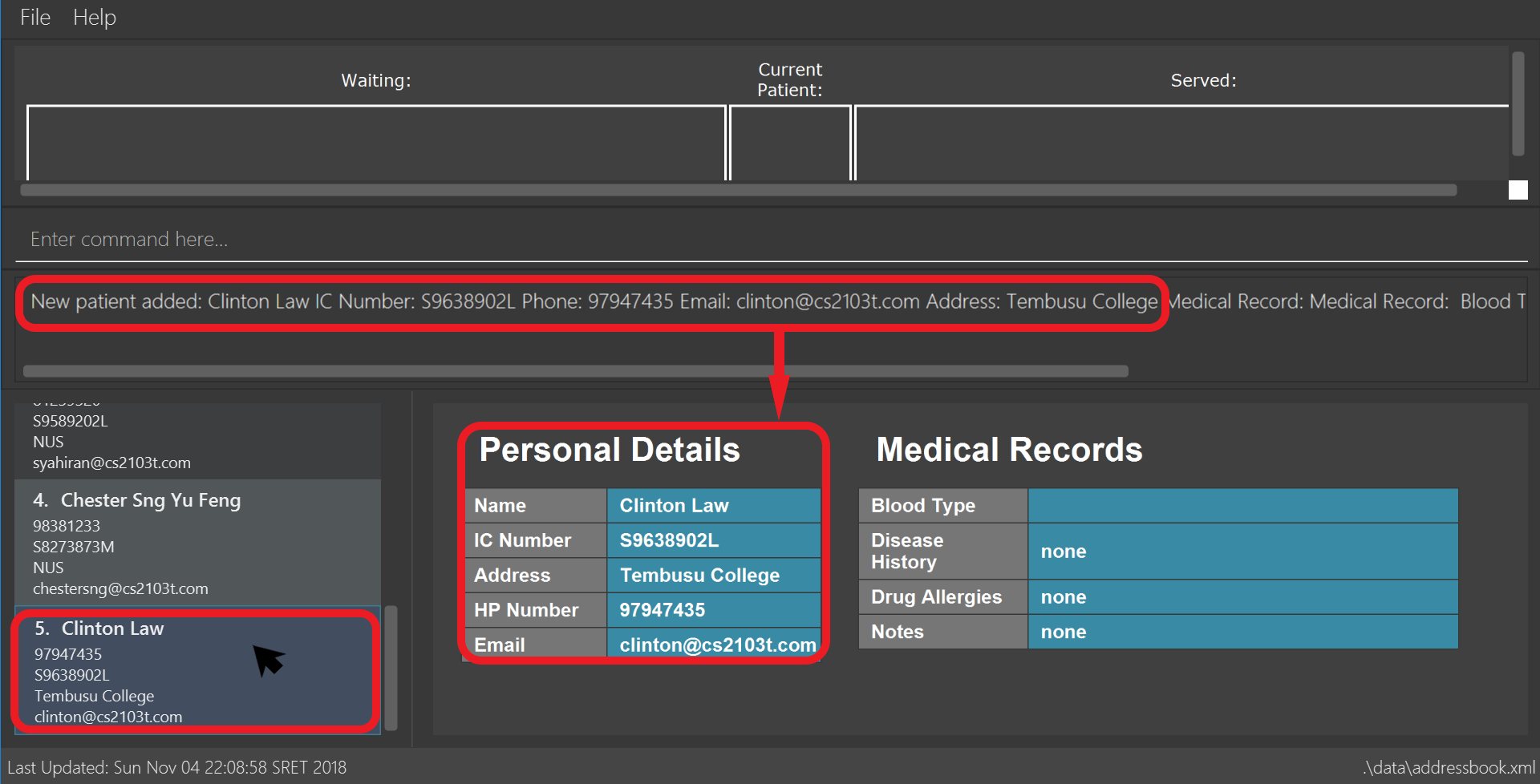
add command specified above and left clicking Clinton’s patient card in the patient list on the left, indicated by the black cursor.3.1.2. Editing a patient: edit
Uhoh! Made a mistake keying in a patient’s particulars? Or perhaps a patient had recently changed his address?
Fret not! Simply update his particulars using the edit command!
Alias: e
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
|
Thing(s) to note:
|
|
Pro tip(s):
You can remove all of a patient’s tags by typing the t/ prefix without specifying any tags.
|
Upon successful execution, you should see the patient’s details updated in the patient list on the left.
Examples:
-
edit 5 p/98534228 e/clawyq@cs2101.com
Updates the phone number and e-mail address of the 5th patient in the list to98534228andclawyq@cs2101.comrespectively, as shown below.
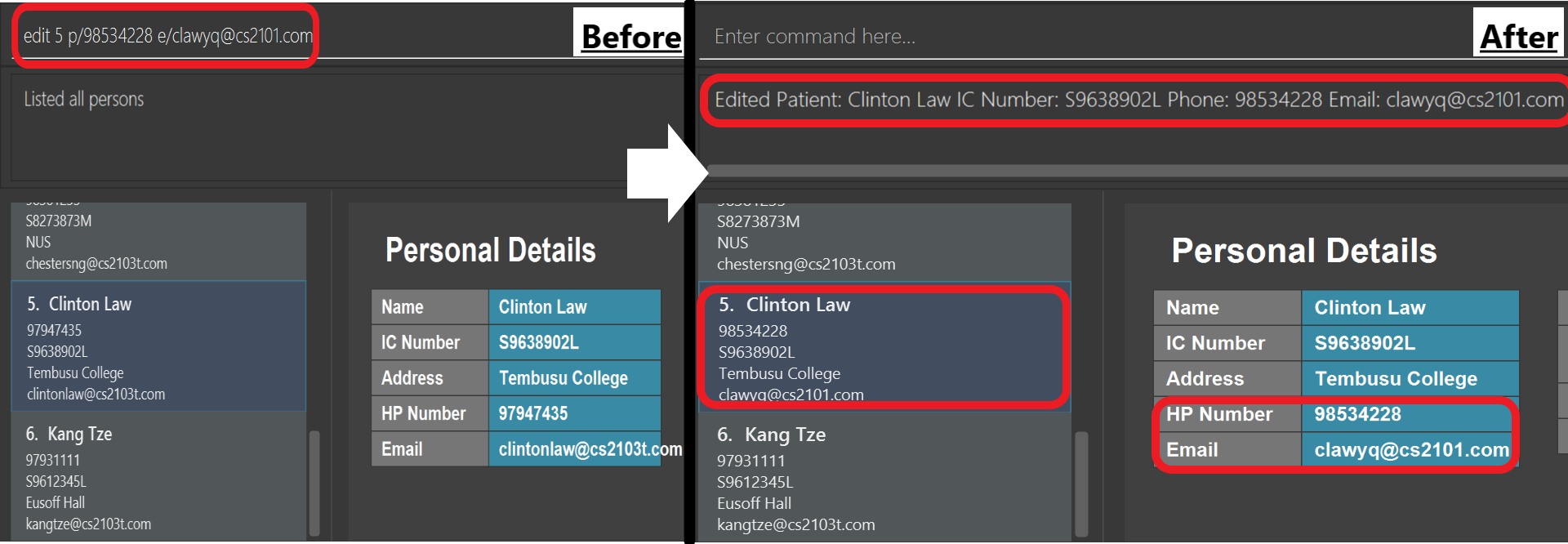
edit command specified above.3.1.3. Locating a patient by name: find
Can’t find the patient you’re looking for amidst the other patient records?
Simply search for the desired patient using the find command!
Alias: f
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
|
Thing(s) to note:
|
|
Pro tip(s):
|
Upon successful execution, you should only see all the patients who have the specified keyword in their names in the patient list on the right.
Examples:
-
f yu
Sieves out all the patients who haveyuin their names.
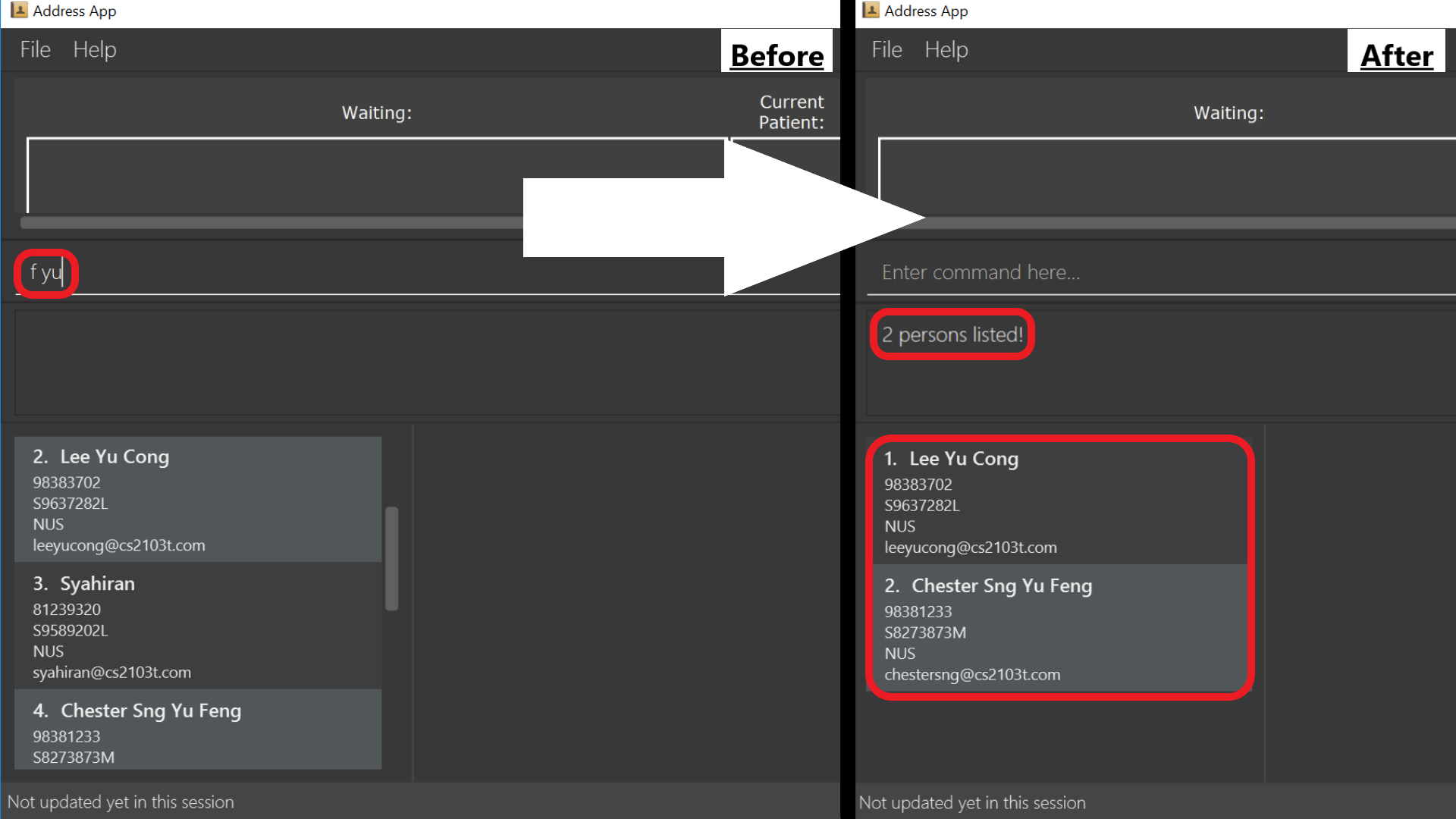
find command specified above via its alias f.3.1.4. Listing all patients: list
Need to list all patients in the database?
Do this easily with the list command.
Alias: l
Format: list
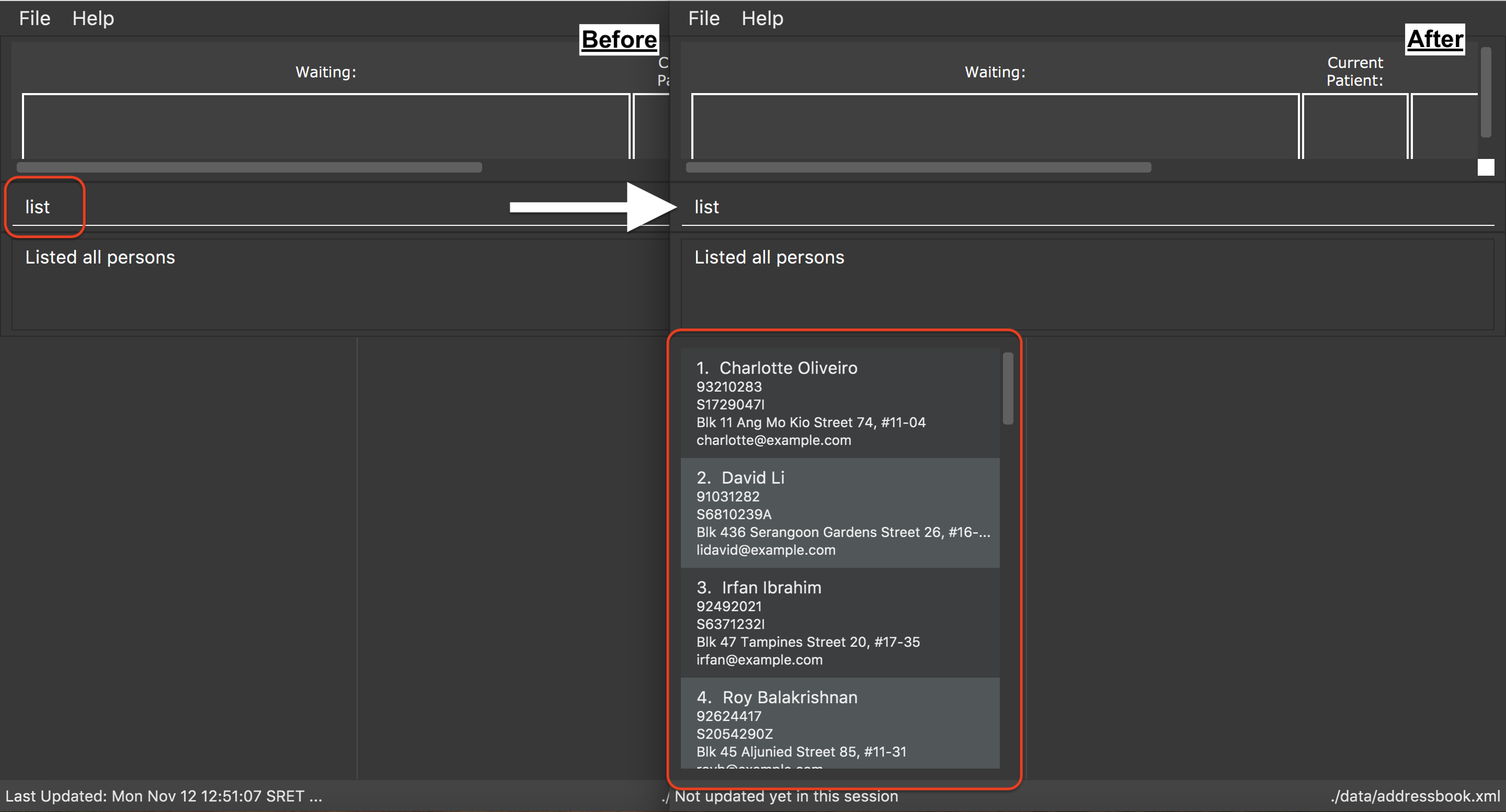
list command3.1.5. Deleting a patient: delete
What if we need to remove a patient’s details from the database?
You can do so with the delete command, which will clear the user’s details from the database completely.
Alias: d
Format: delete INDEX
|
Thing(s) to note:
|
|
Pro tip(s):
Deletes the patient at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed patient list. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
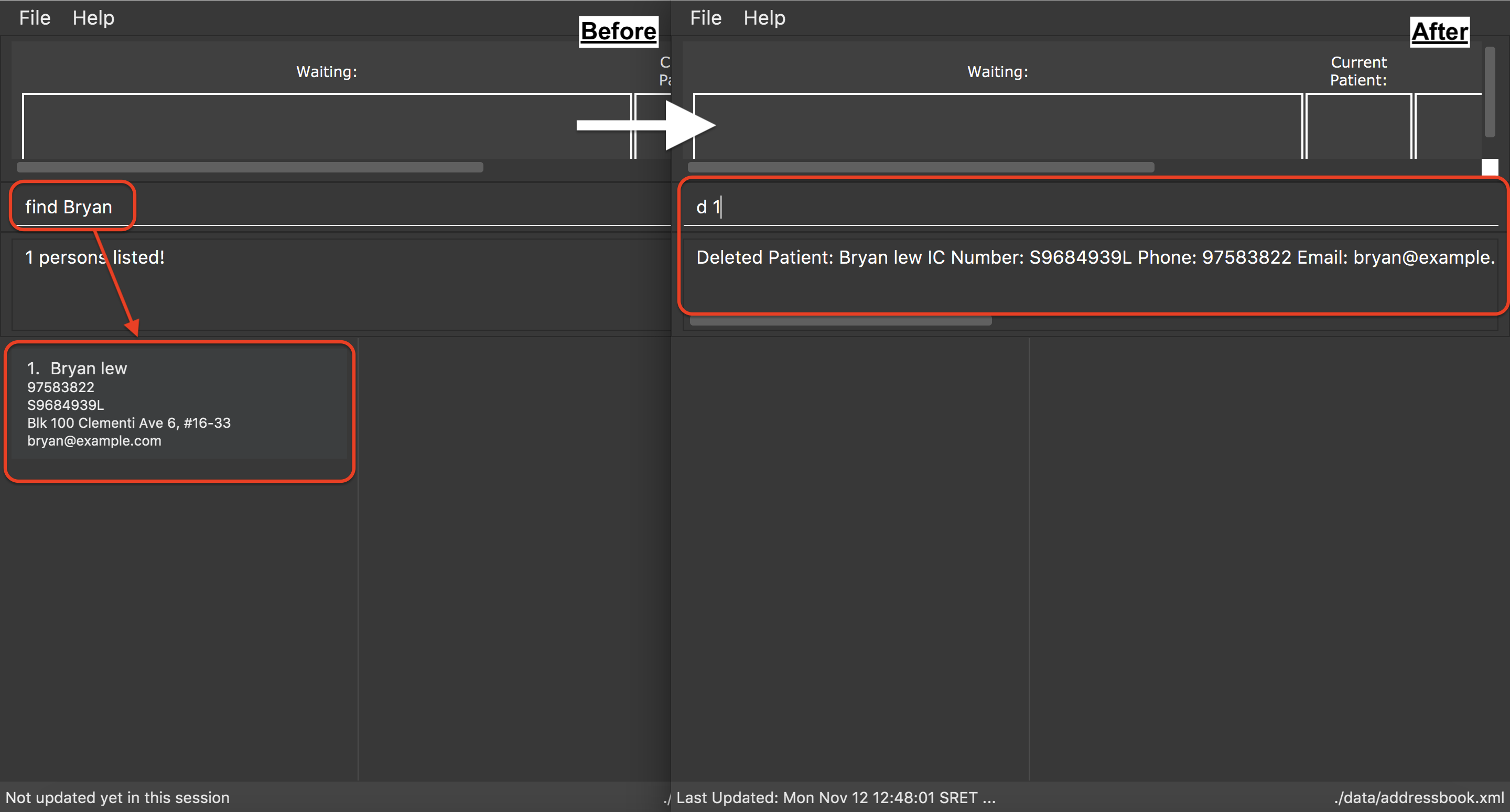
Examples:
-
list
delete 2
Deletes the 2nd patient in the database. -
find Bryan
d 1
Deletes the 1st patient in the resulting list of thefindcommand.
find Bryan and d 1 command3.1.6. Selecting a patient: select
Need a more detailed view of a patient? Use the select command to view a patient’s profile!
Alias: s
Format: select INDEX
|
Pro tip(s):
Selects the patient at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed patient list. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
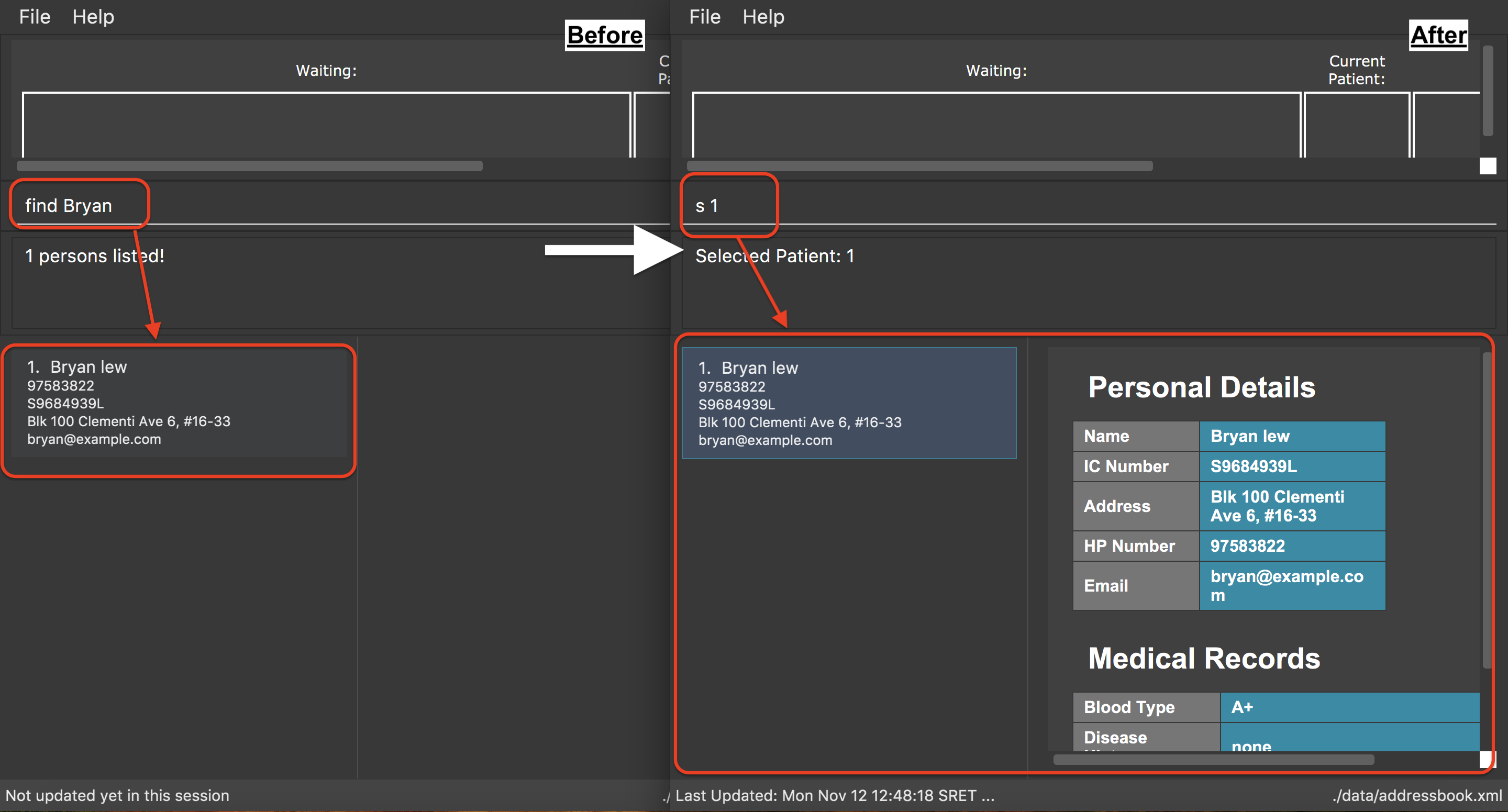
Examples:
-
find Bryan
s 1
Selects the 1st patient in the resulting list of thefindcommand.
find Bryan and s 1 command.3.1.7. Adding medical records of a patient: addmedicalrecord
Updating a patient’s MedicalRecord on the fly is easy! Just use the addMedicalRecord command!
Alias: amr
Format: addmedicalrecord INDEX [b/BLOOD_TYPE] [d/PAST_DISEASES]… [da/DRUG_ALLERGY]… [m/NOTE]…
|
Pro tip(s):
|
Examples:
-
addmedicalrecord 5 da/Paracetamol d/Diabetes
AddsParacetamol(under Drug Allergy) andDiabetes(under Past Diseases) to theMedicalRecordof the 5th patient.
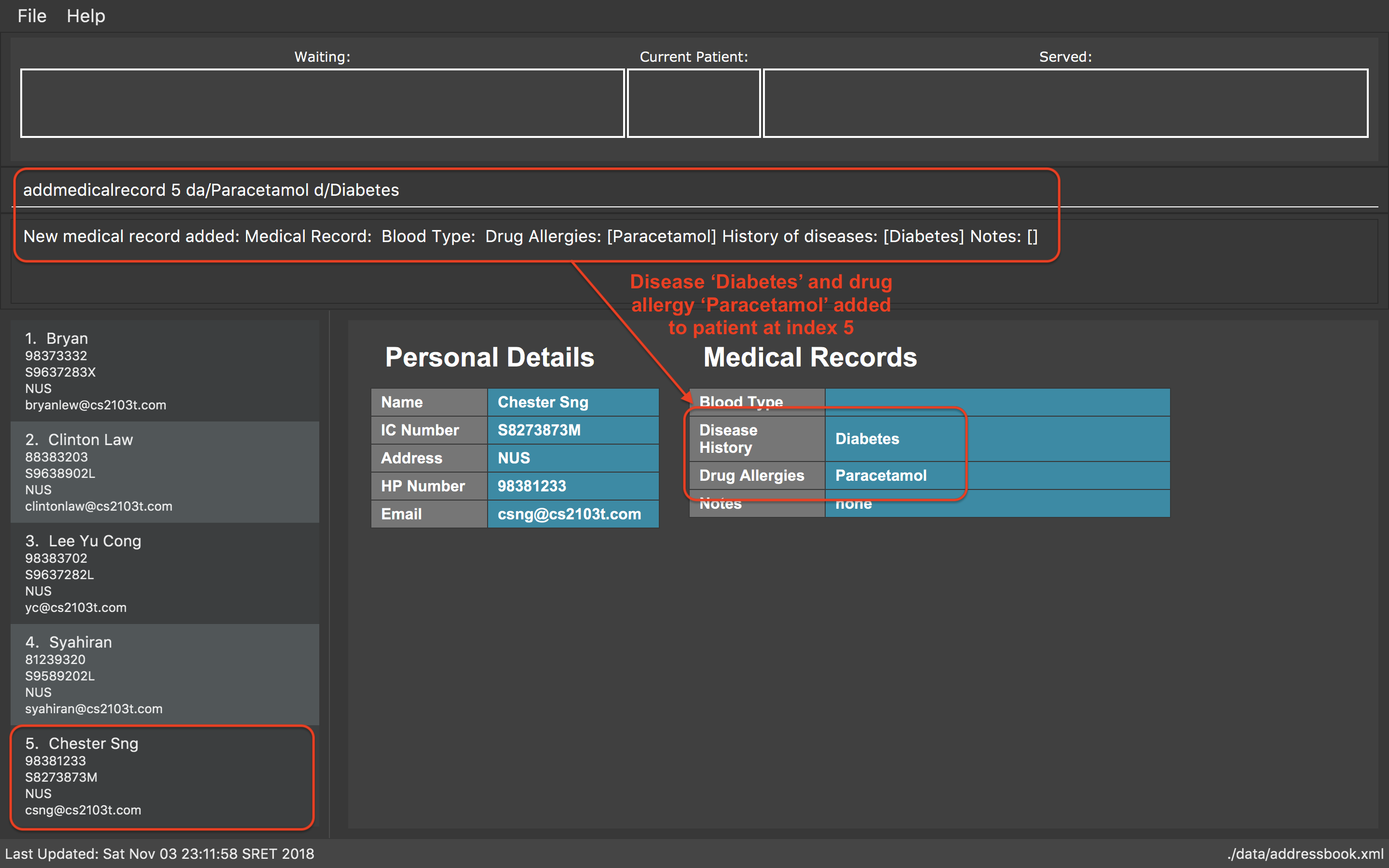
addmedicalrecord 5 da/Paracetomal d/Diabetes command-
amr 3 b/B+
AddsB+(under Blood Type) to theMedicalRecordof the 3rd patient.
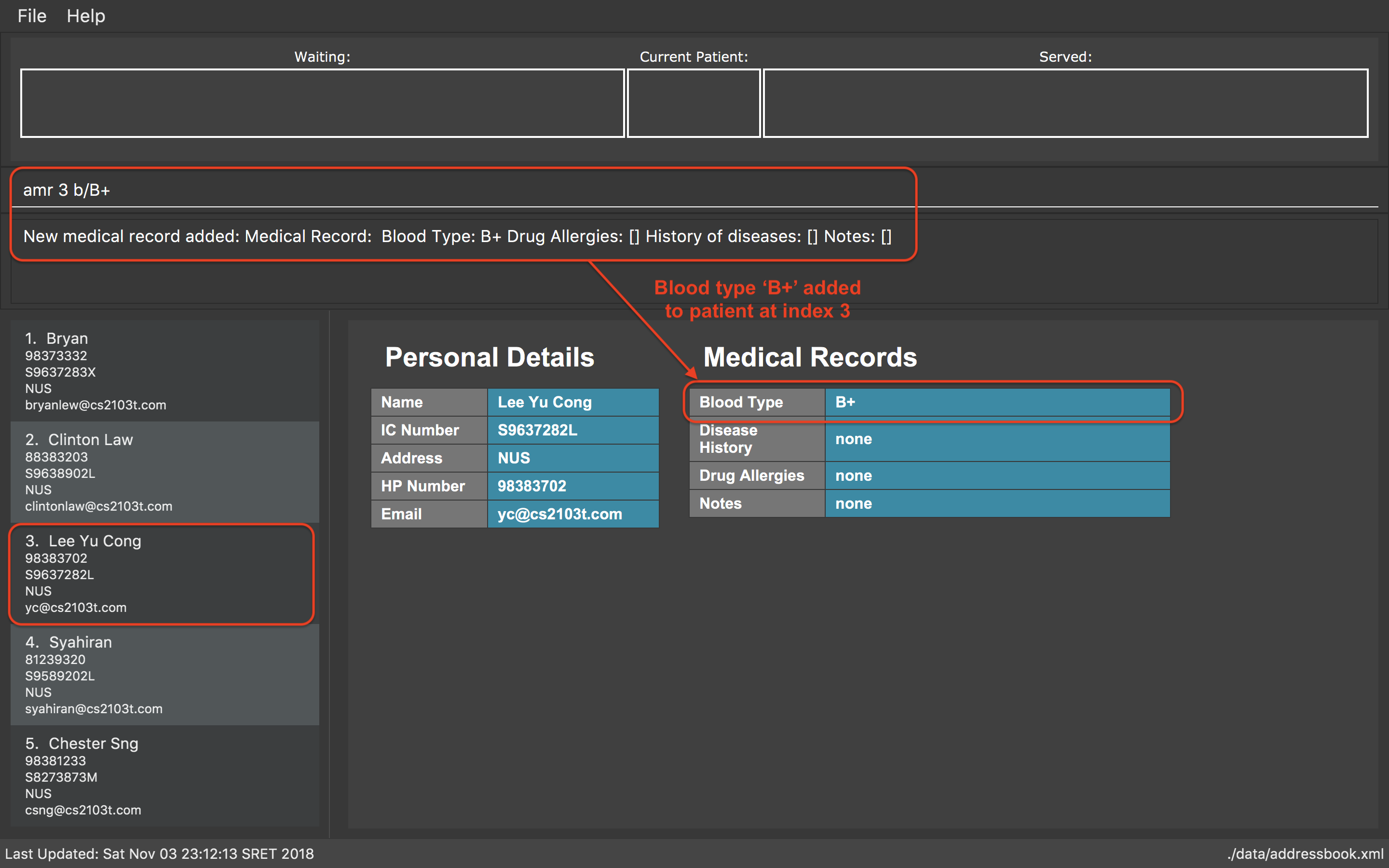
amr 3 b/B+ command3.2. Medicine Records System
3.2.1. Adding a medicine: addmedicine
Bought the latest medicine that effectively cures eczema?
Use addmedicine to add that medicine into CLInic now!
Alias: am
Format: addmedicine mn/MEDICINE_NAME msq/MINIMUM_STOCK_QUANTITY ppu/PRICE_PER_UNIT sn/SERIAL_NUMBER s/STOCK
|
Example:
-
addmedicine mn/panadol msq/500 ppu/0.50 sn/91853 s/1000
Adds a medicine namedpanadolwith minimum stock quantity of500units, price per unit of$0.50, serial number of91853and stock of1000units to the CLInic inventory. -
am mn/asprin msq/100 ppu/0.20 sn/53068 s/100
Adds a medicine namedasprinwith minimum stock quantity of100units, price per unit of$0.20, serial number of53068and stock of100units to the CLInic inventory.
See below for a pictorial guide on how to add aspirin to the records:
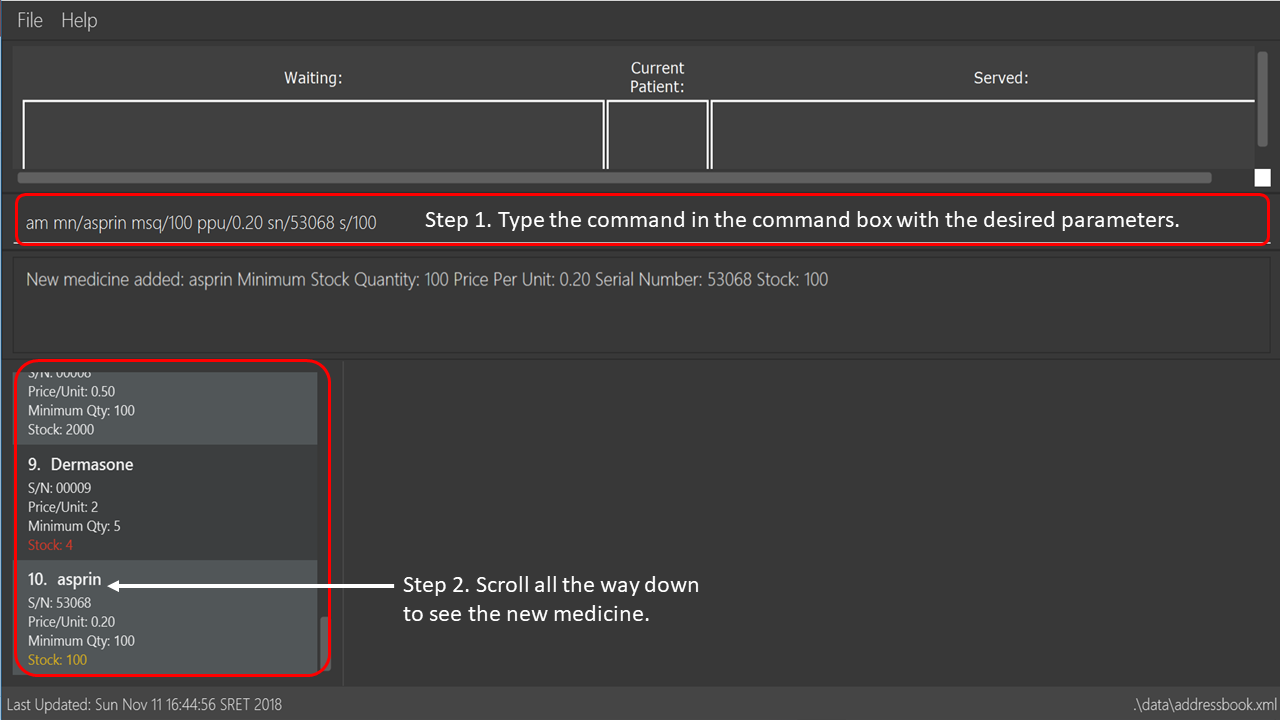
addmedicine command3.2.2. Editing a medicine: editmedicine
Edits the details of an existing medicine.
Alias: em
Format: editmedicine INDEX [mn/MEDICINE_NAME] [msq/MINIMUM_STOCK_QUANTITY] [ppu/PRICE_PER_UNIT] [sn/SERIAL_NUMBER] [s/STOCK]
|
Pro tip(s):
|
Example:
-
editmedicine 1 mn/hydrazine s/1500
Renames the medicine at index 1 tohydrazinewhilst updating its stock to1500. -
em 1 sn/91853
Updates the serial number of the medicine at index 1 to91853.
3.2.3. Restocking a medicine: restock
Restocks an existing medicine with additional quantity.
Alias: rs
Format: restock INDEX amt/AMOUNT
|
Pro tip(s):
Restocks the medicine at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed medicine list. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Example:
-
restock 2 amt/123
Adds123additional units of the 2nd medicine to the clinic’s current stock. -
rs 3 amt/500
Adds500additional units of the 3rd medicine to the clinic’s current stock.
3.2.4. Listing all medicines: liststock
Lists all medicine information in the CLInic medicine inventory.
Alias: ls
Format: liststock
3.2.5. Finding details of a medicine: findmedicine
Need the price of a medicine urgently?
Use findmedicine to search for
the details of a medicine from its medicine name!
Alias: fm
Format: findmedicine MEDICINE_NAME
|
You can enter more than one name to get the results of all medicines with the names entered. Refer to the third example below. |
Example:
-
findmedicine panadol
Finds the details of the medicines with the name panadol. -
fm chlorpheniramine
Finds the details of the medicines with the name chlorpheniramine. -
fm telfast panadol
Finds the details of all medicines with the name telfast or panadol.
See below for a pictorial guide on how to find telfast or panadol in CLInic:
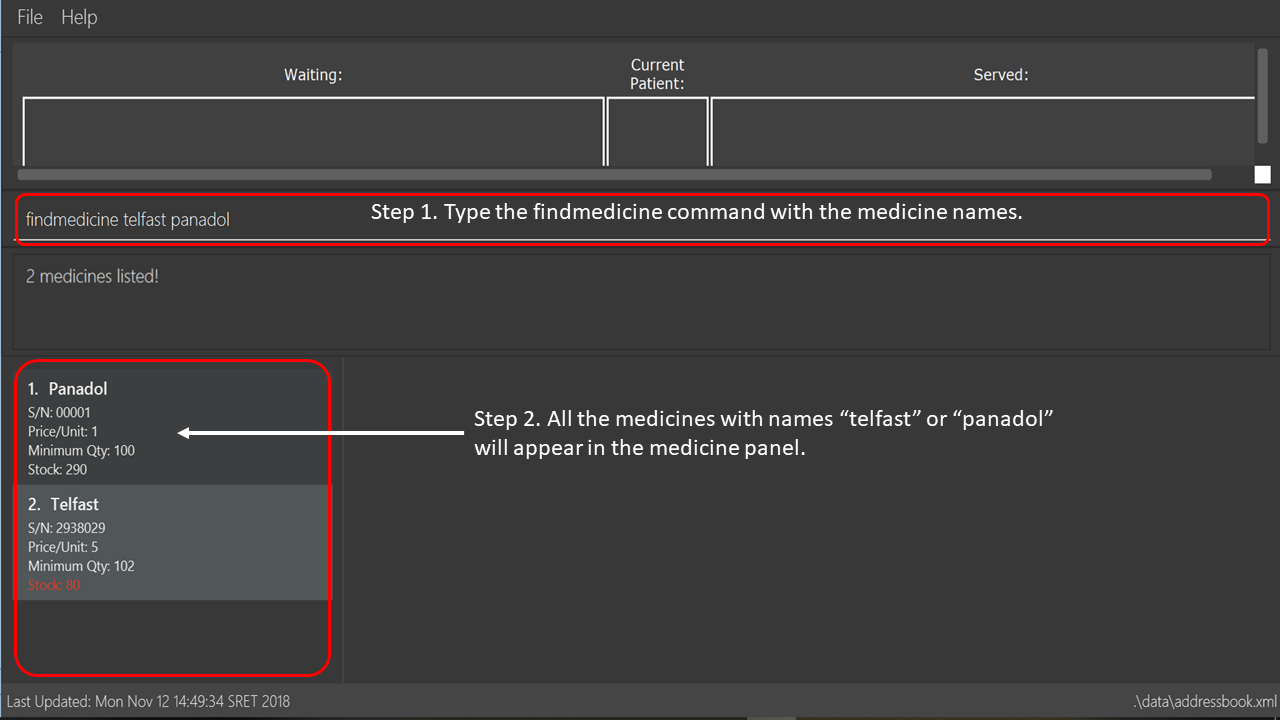
findmedicine command3.2.6. Listing medicines that are low in supply: checkstock
No time to do stock taking?
Use checkstock and get it done in under 2 seconds!
Alias: cs
Format: checkstock
| Medicines that are low in supply are defined as those whose stock levels are lower than or equal to their minimum stock quantities. |
See below for a pictorial guide on how to use checkstock:
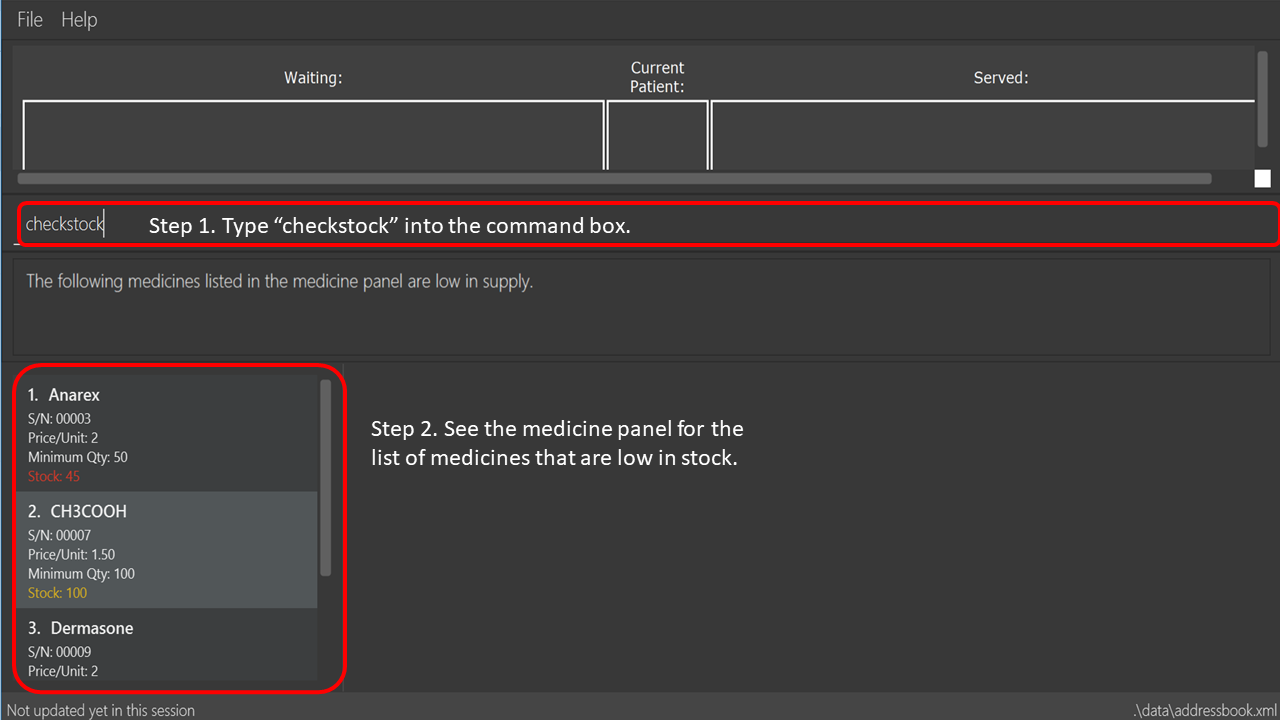
checkstock command3.3. Queue Management
You cannot use edit, delete, addmedicalrecord commands on a patient that is in queue. If the patient’s details are changed when
the patient is in queue, the patient will be removed from queue.
|
3.3.1. Registering a patient to Waiting Queue: register
A patient needs to see the doctor? Better get him into the queue using this command!
Alias: reg
Format: register INDEX
|
Pro tip(s):
Registers the patient at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed patient list. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Example:
-
list
register 3
Registers the 3rd patient in the database.
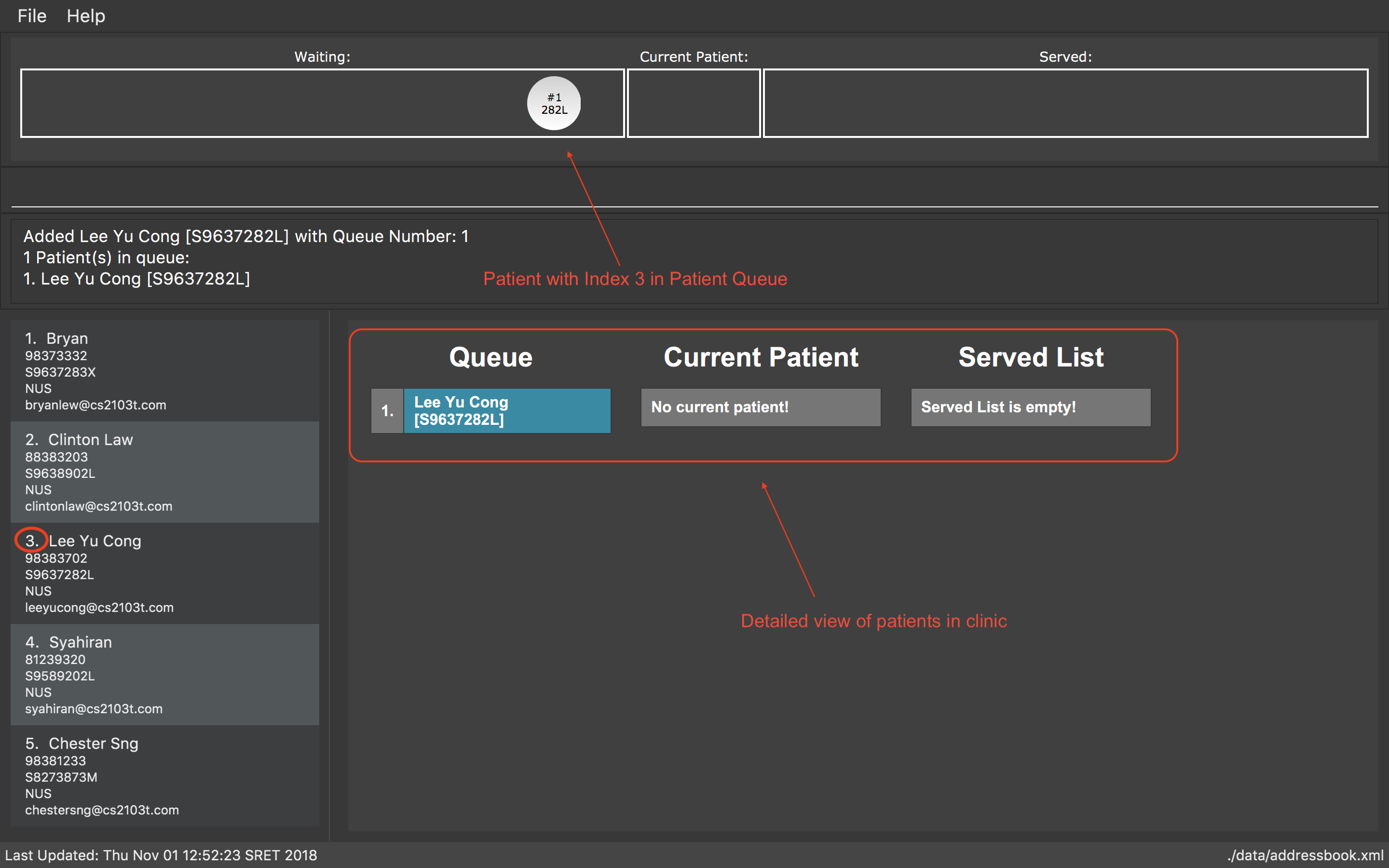
register 3 command-
find david
reg 1
Registers the 1st patient in the resulting list of thefindcommand.
3.3.2. Listing all patients in Waiting Queue: queue
Need to know who is in the queue? Use the queue command!
Alias: q
Format: queue
3.3.3. Removing a patient from Waiting Queue: remove
Patient can’t wait for his turn and left the clinic? Time to remove him from the queue!
Alias: rem
Format: remove INDEX
|
Pro tip(s):
Removes the patient at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed patient list. The INDEX must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
remove 3
Removes the 3rd patient in the queue.
remove 3 command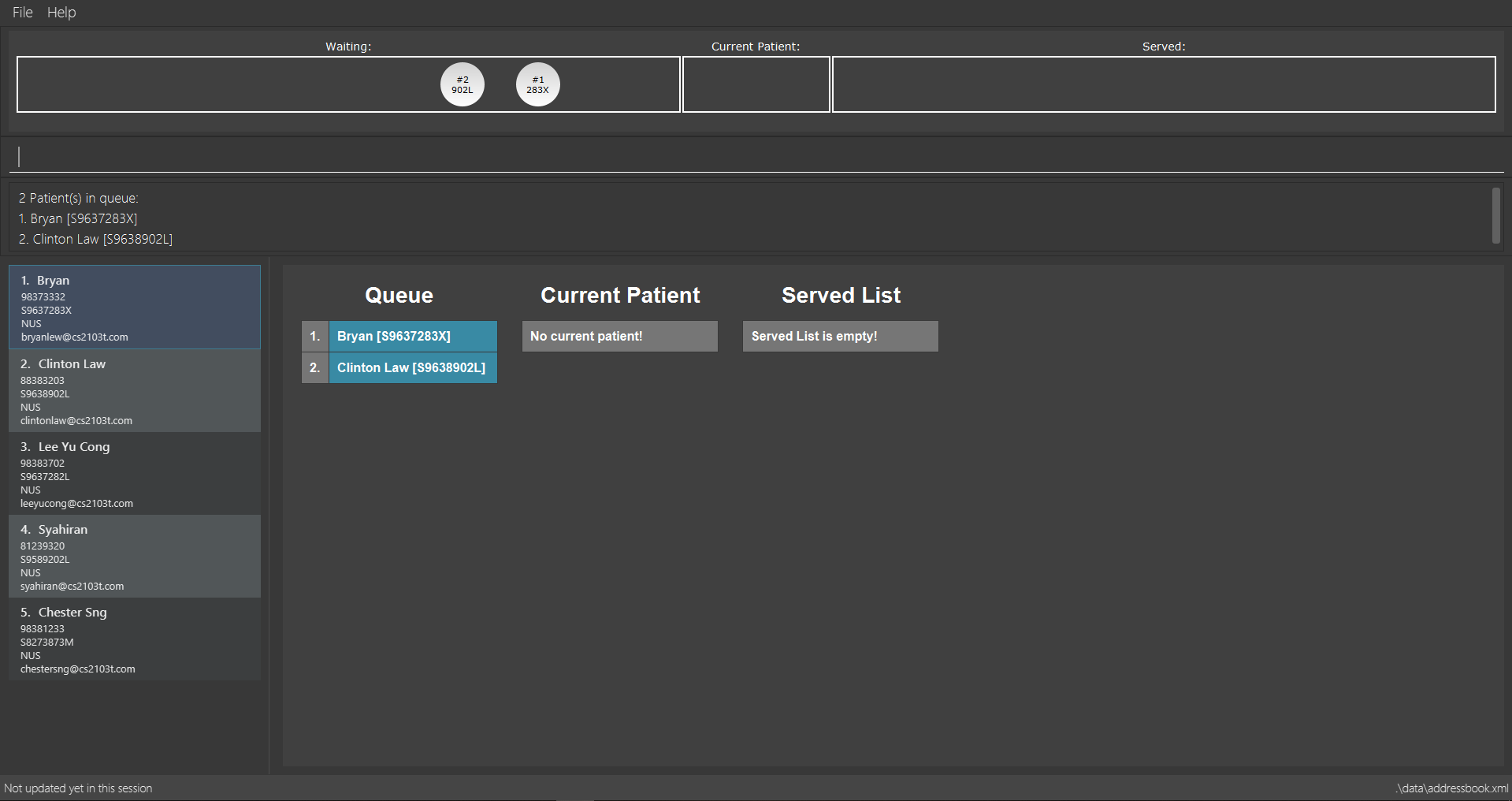
remove 3 command-
rem 3
Removes the 2nd patient in the queue.
3.3.4. Inserting a patient to Waiting Queue: insert
Insert a patient into any position using this command!
Alias: ins
Format: insert INDEX p/POSITION
|
Pro tip(s):
|
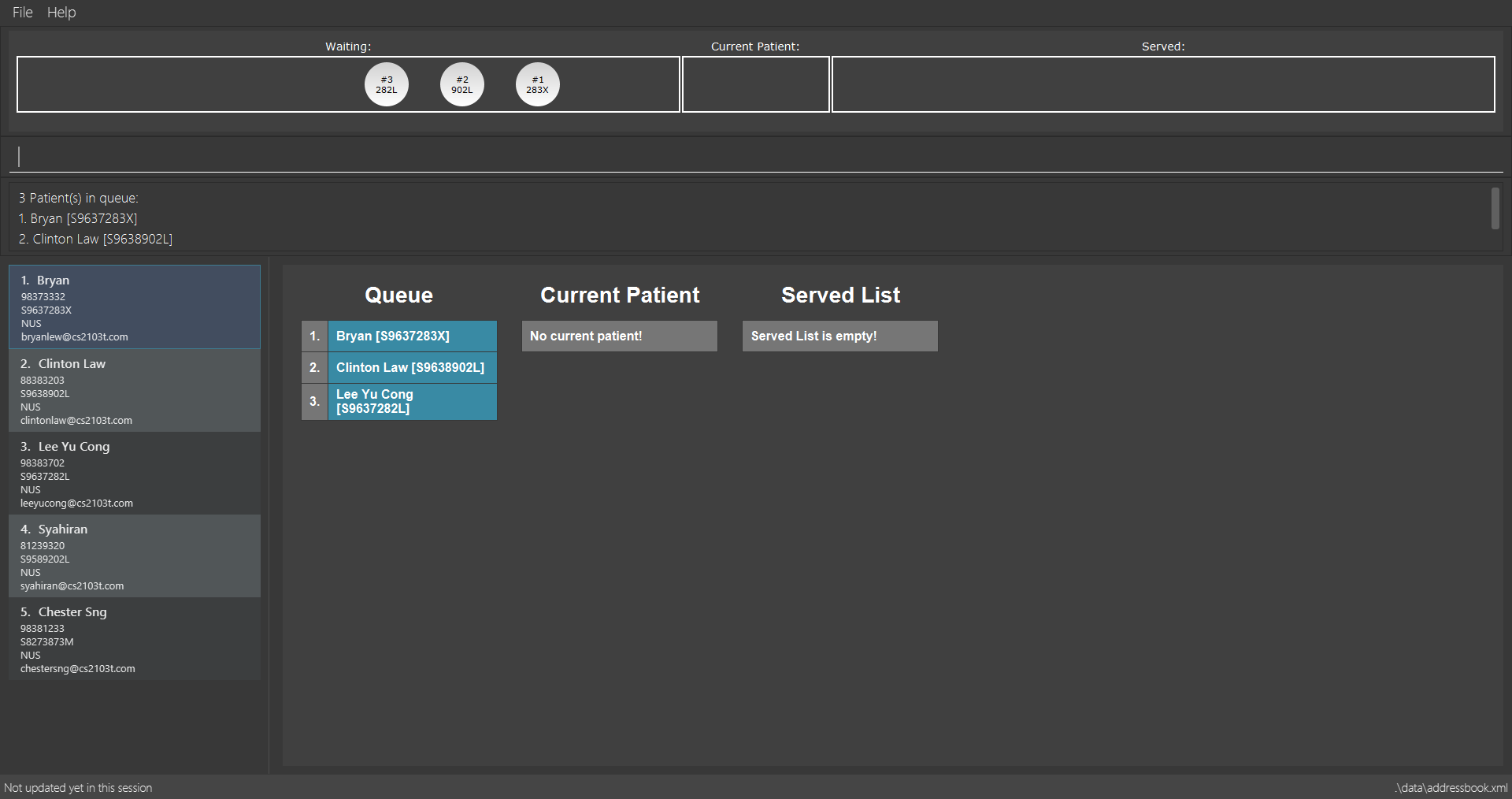
Examples:
-
list
insert 4 p/2
Inserts the 4th patient in the database into the 2nd position in the patient queue.
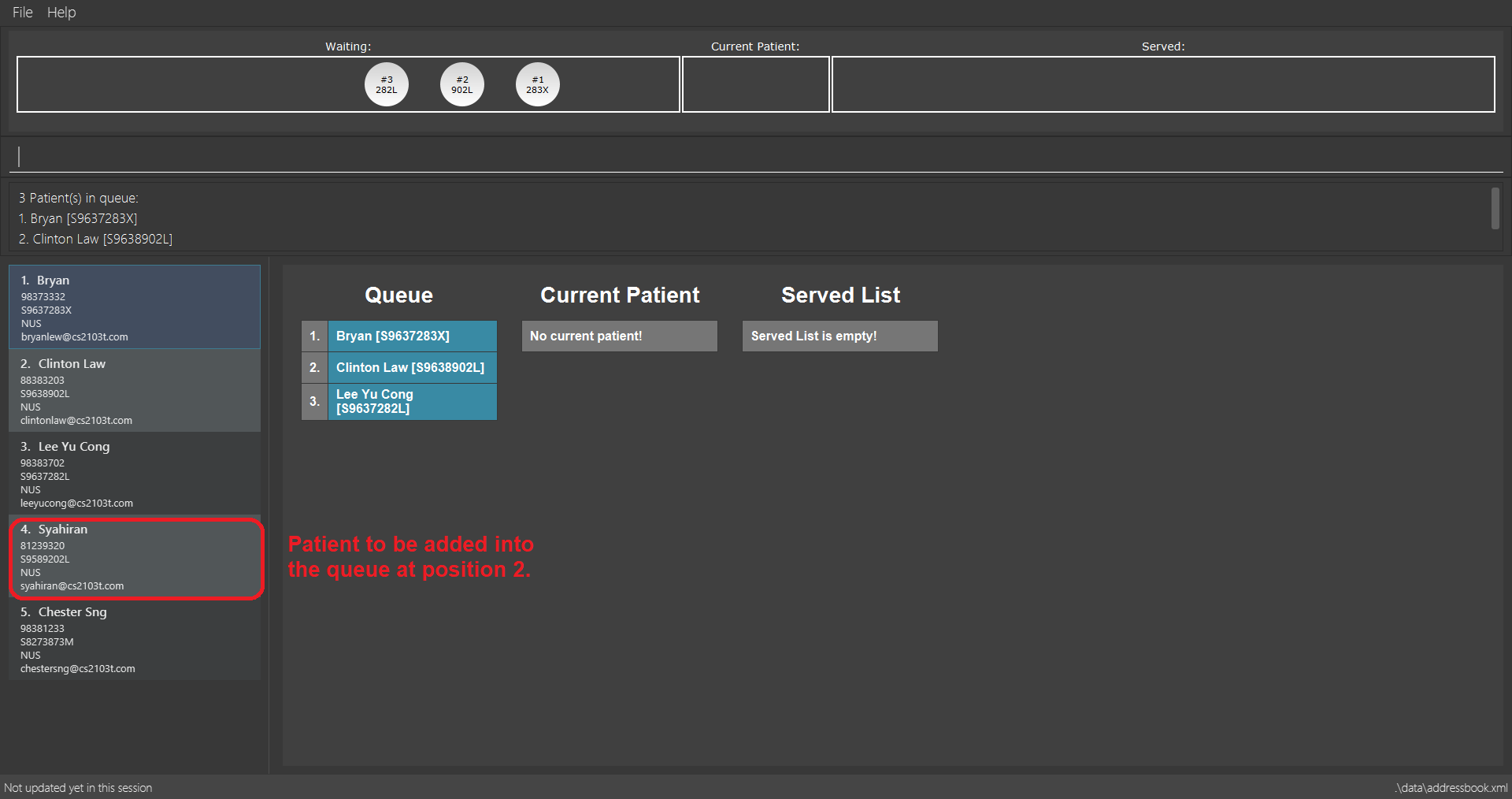
insert 4 p/2 command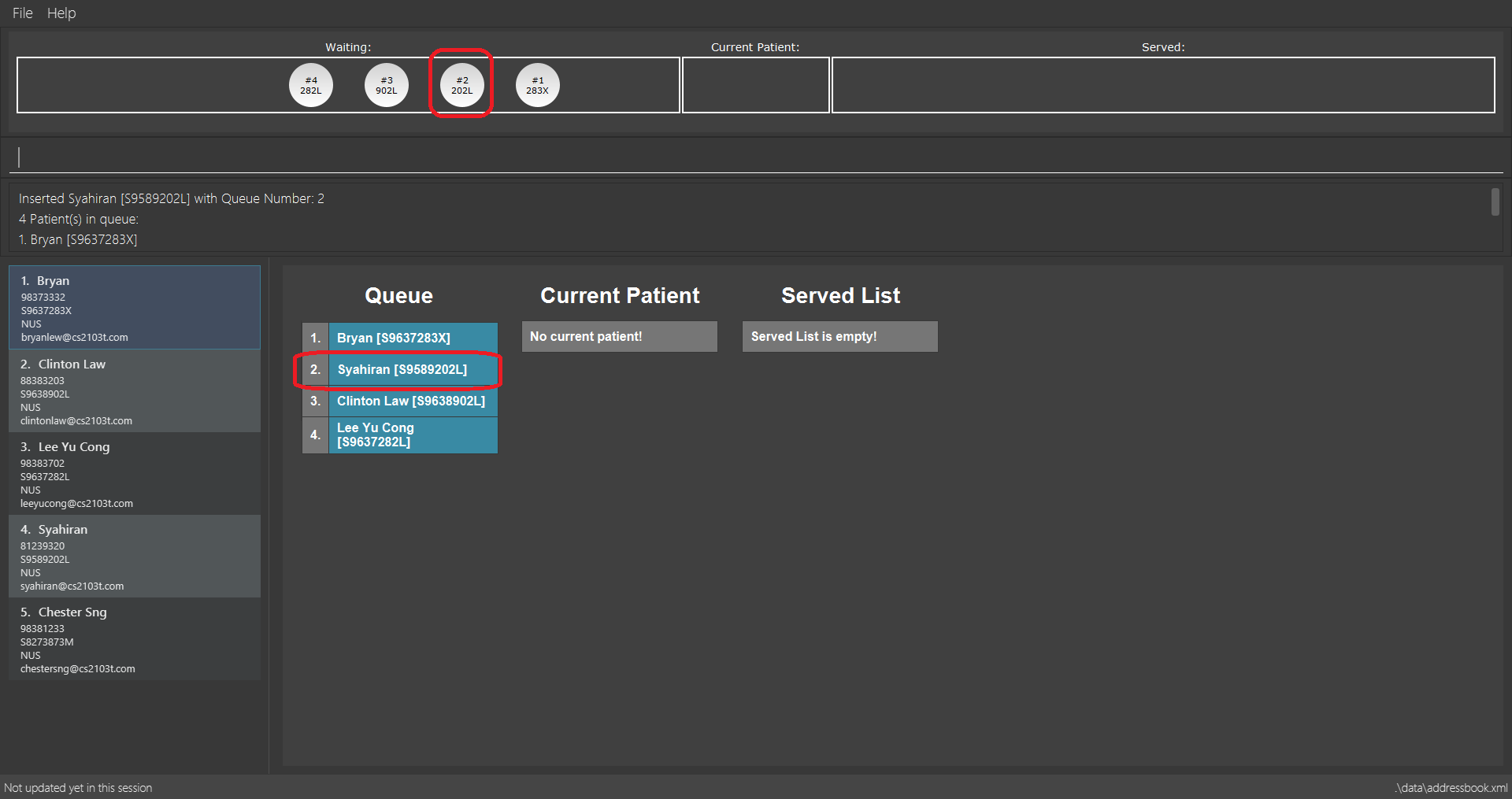
insert 4 p/2 command-
ins 3 p/5
Inserts the 3rd patient into the 5th position in the patient queue.
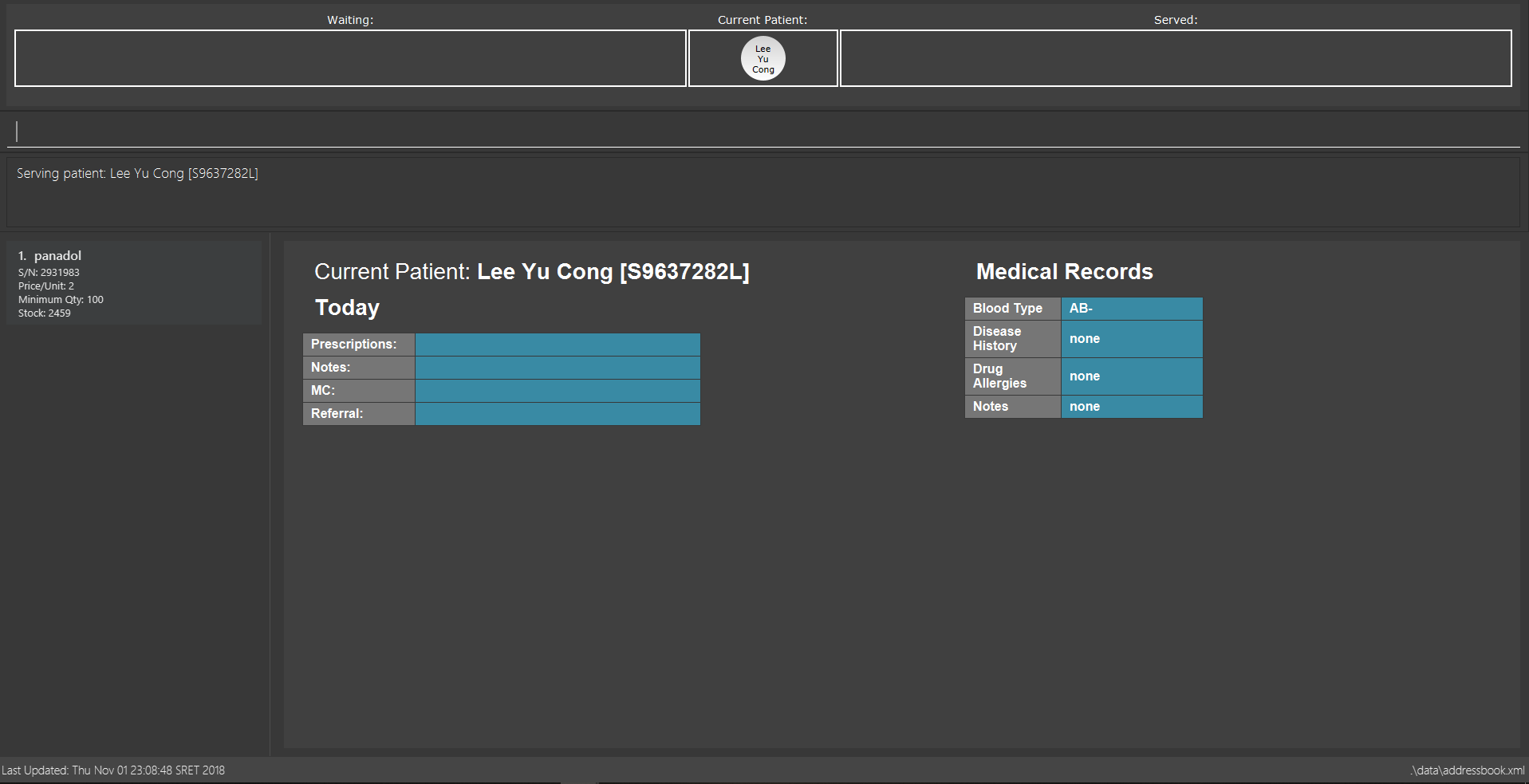
3.3.5. Serving the first patient in Waiting queue: serve
Doctor is finally ready to serve the next patient? Use the serve command!
Alias: ser
Format: serve
|
Pro tip(s):
Upon successful call of this command, the medicine list will be displayed.
|
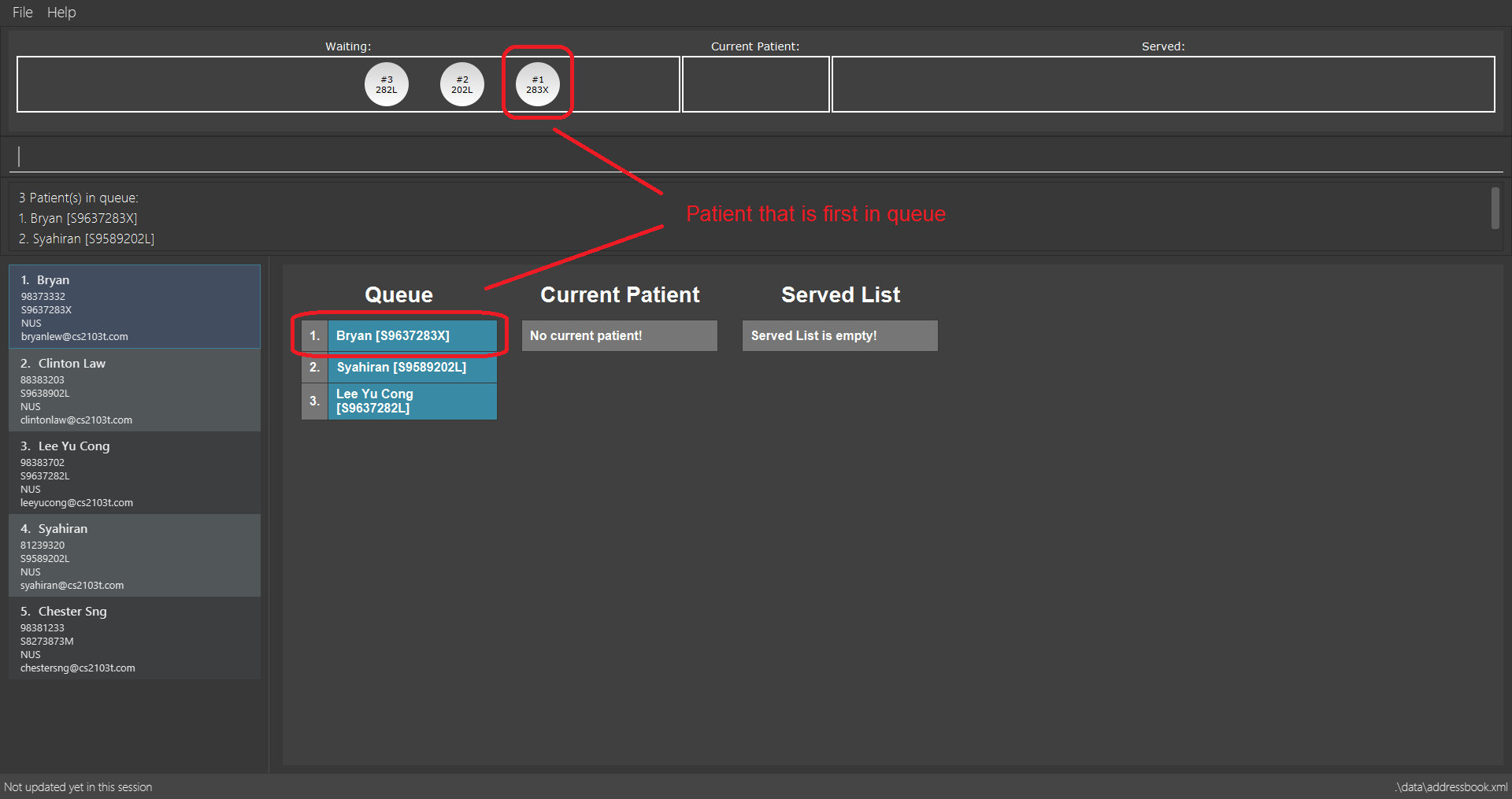
serve command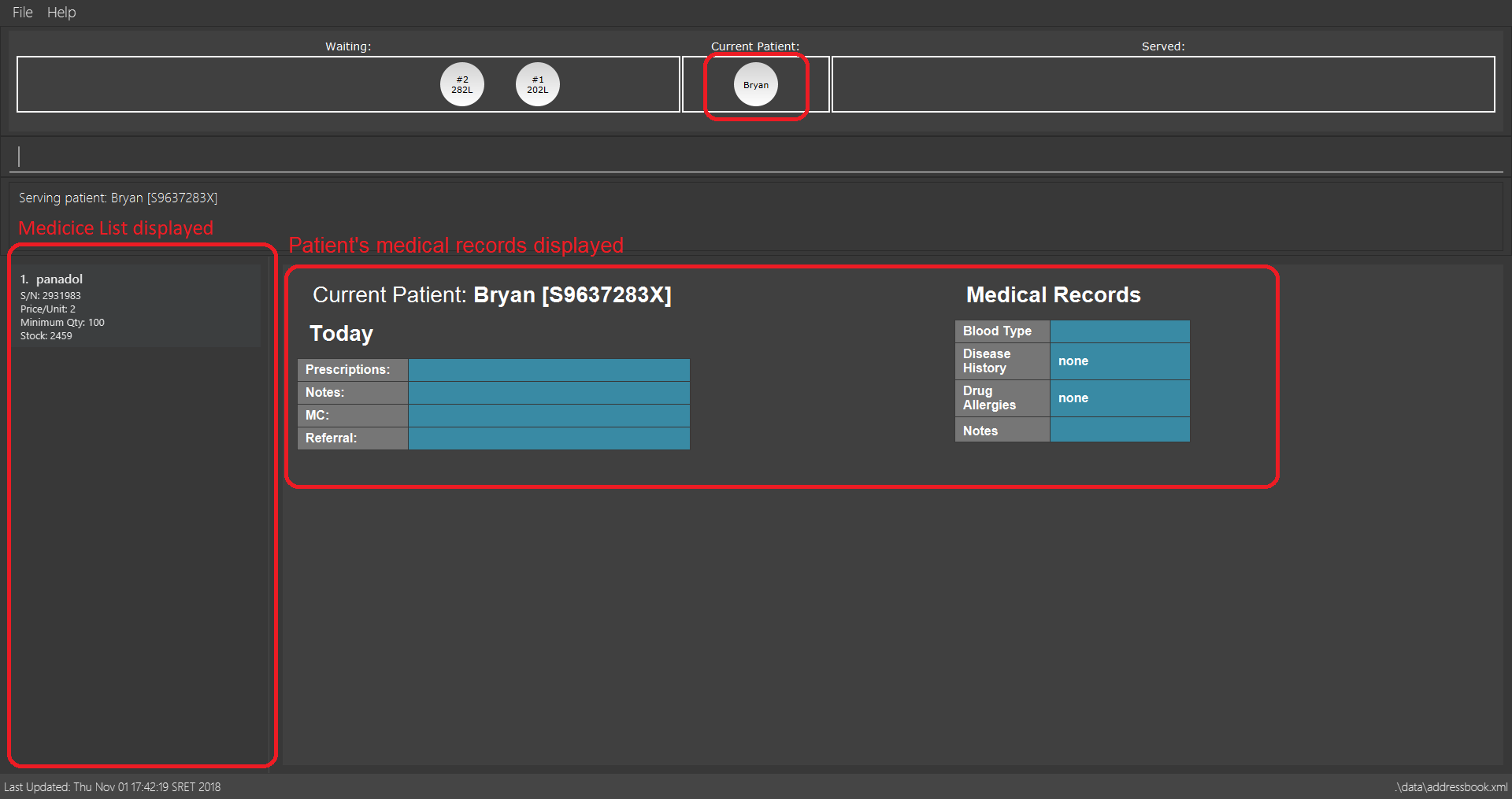
serve command3.3.6. Adding document contents to Current Patient: adddocument
Patient has a bad headache? Patient needs 5 days mc? Better write them down!
Alias: ad
Format: adddocument [mc/MC_DAYS] [n/NOTES] [r/REFERRAL]
|
Pro tip(s):
|
Examples:
-
adddocument mc/3 n/Headache for the past 2 days
Adds MC duration and notes to the Current Patient.
adddocument mc/3 n/Headache for the past 2 days command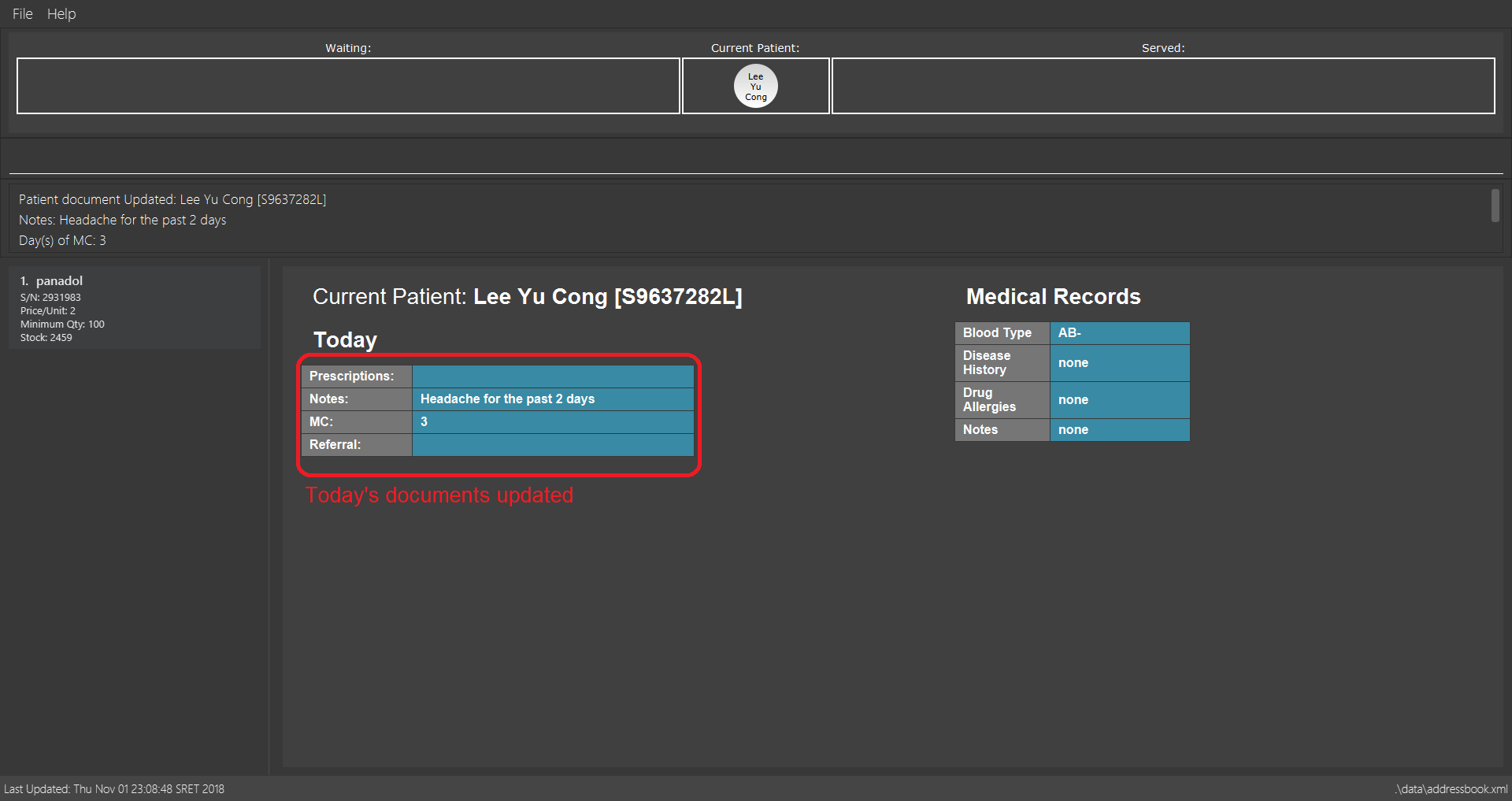
adddocument mc/3 n/Headache for the past 2 days command-
ad r/Ng Teng Fong Hospital
Adds referral to the Current Patient.
3.3.7. Displaying document contents for Current Patient: displaydocuments
What documents have you added to the patient? Use this command to find out!
Alias: dd
Format: displaydocuments
3.3.8. Dispensing medicine to Current Patient: dispensemedicine
An apple a day certainly is not enough! Time to give the patient some medicine!
Alias: dm
Format dispensemedicine MEDICINE_INDEX amt/AMOUNT
|
Pro tip(s):
Dispenses medicine at the specified MEDICINE_INDEX to the Current Patient. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed medicine list. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
dispensemedicine 1 amt/10
10 units of the 1st medicine in the displayed medicine list will be added to the Current Patient.
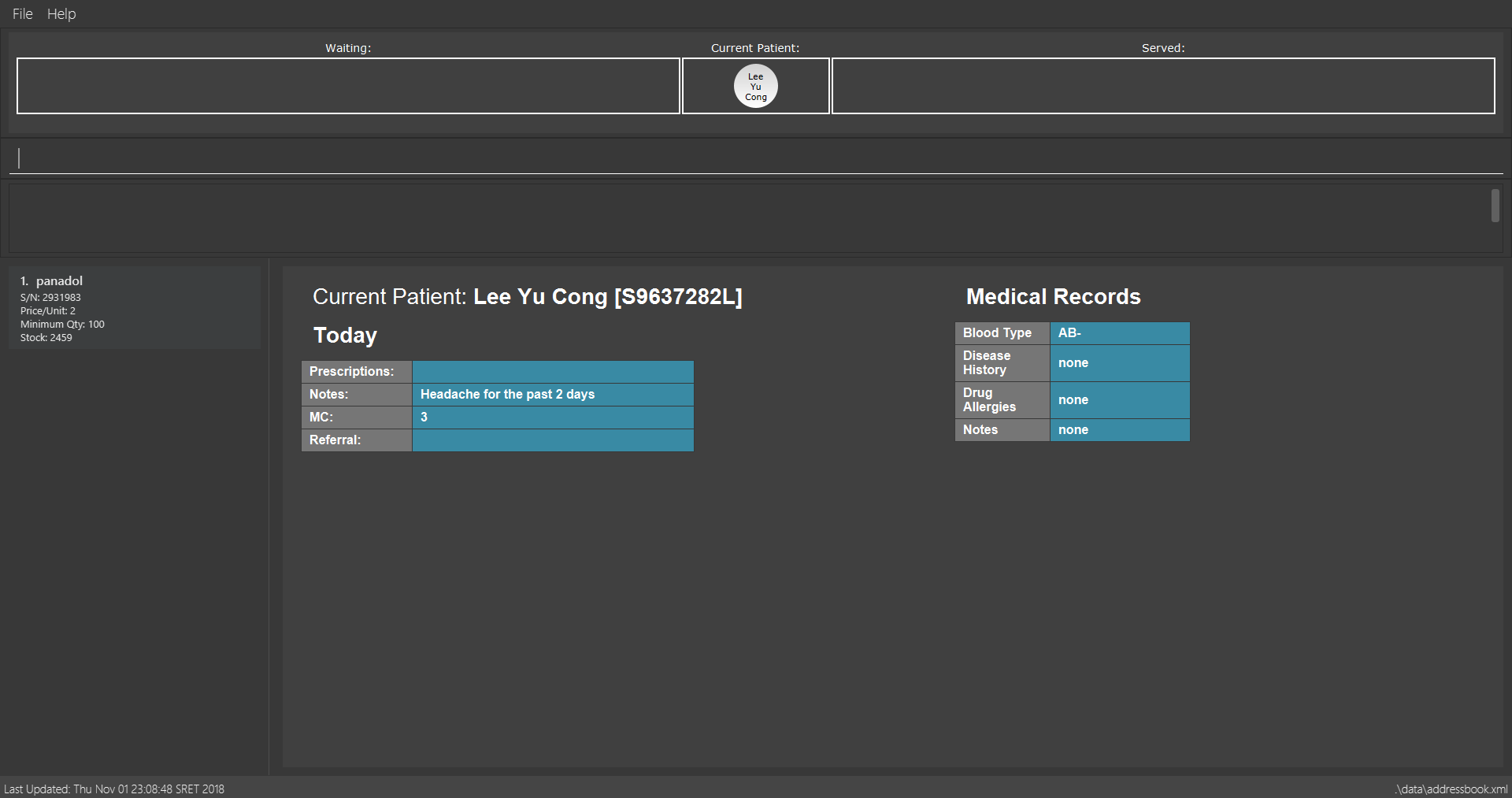
dispensemedicine 1 amt/10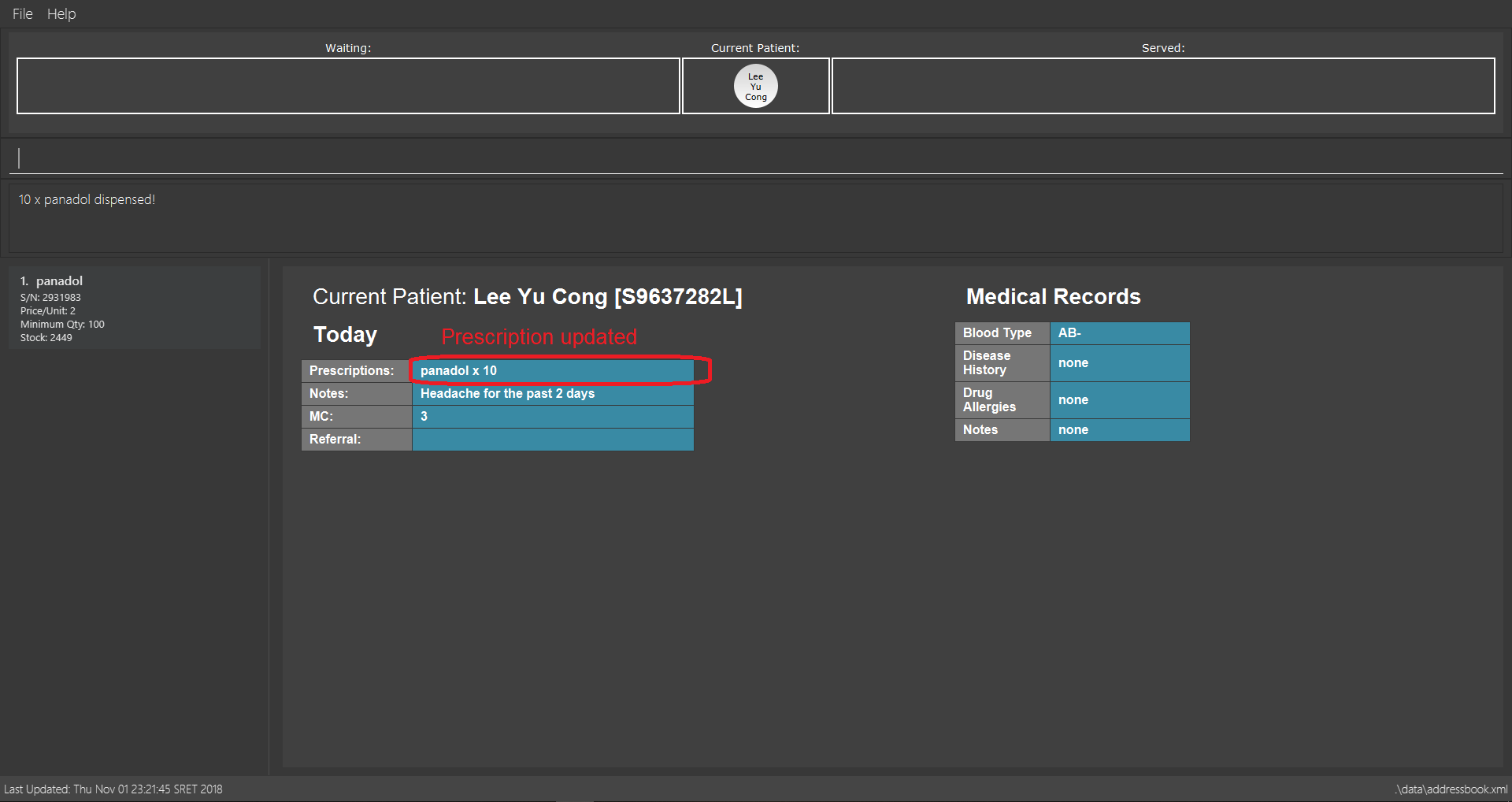
dispensemedicine 1 amt/10-
dm 5 amt/2
2 units of the 5th medicine in the displayed medicine list will be added to the Current Patient.
3.3.9. Finishing service of the Current Patient: finish
Looks like we are done with the patient!
Format: finish
|
Pro tip(s):
|
3.3.10. Removing patient from Served Patient Queue: payment
Done with all document processing? Patient can now make his payment and leave. Goodbye!
Alias: pay
Format: payment INDEX
|
Pro tip(s):
Removes the patient at the specified INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the Served Patient Queue. The index must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
payment 3
Removes the 3rd patient from the Served Patient Queue.
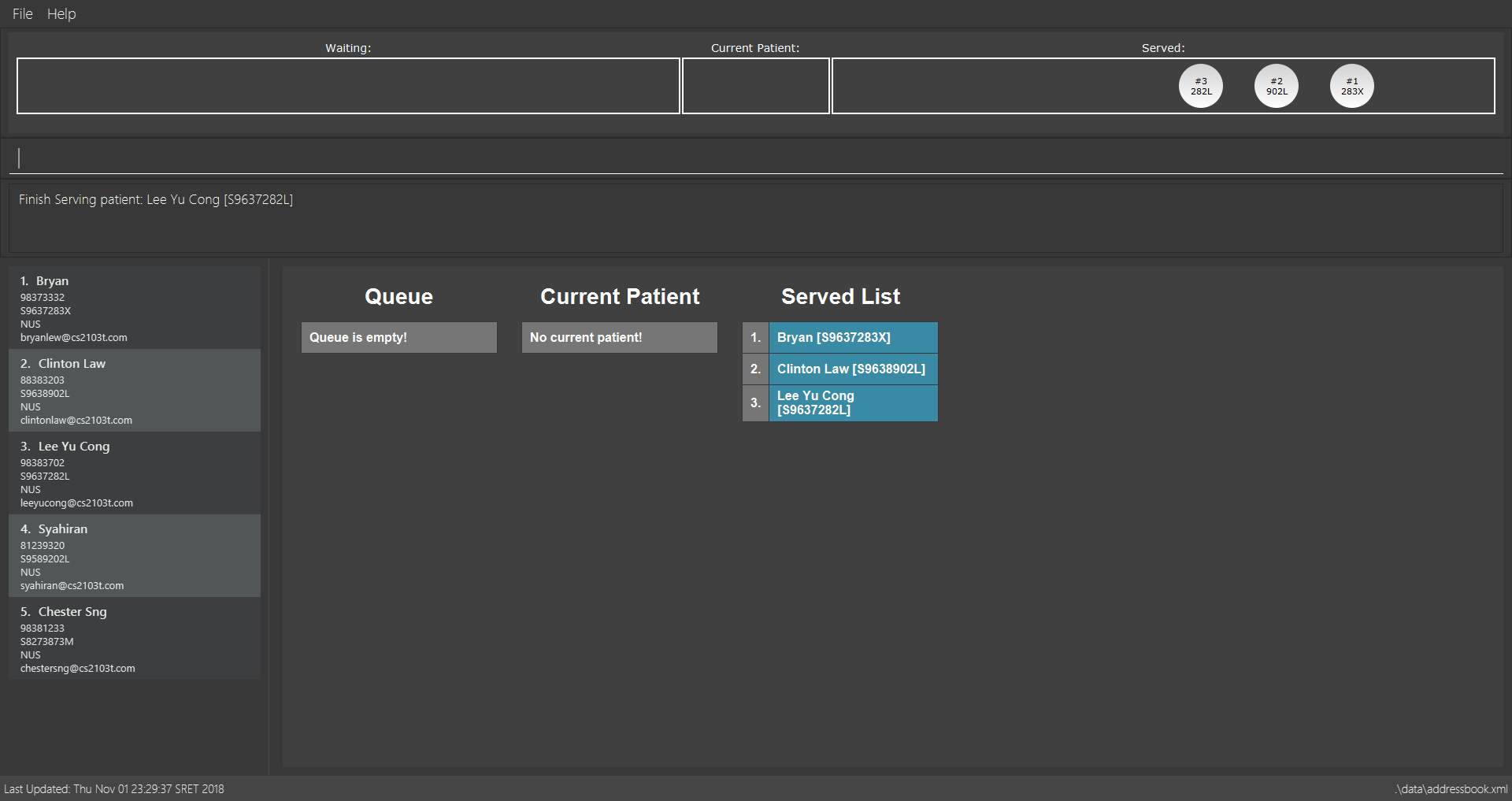
payment 3 command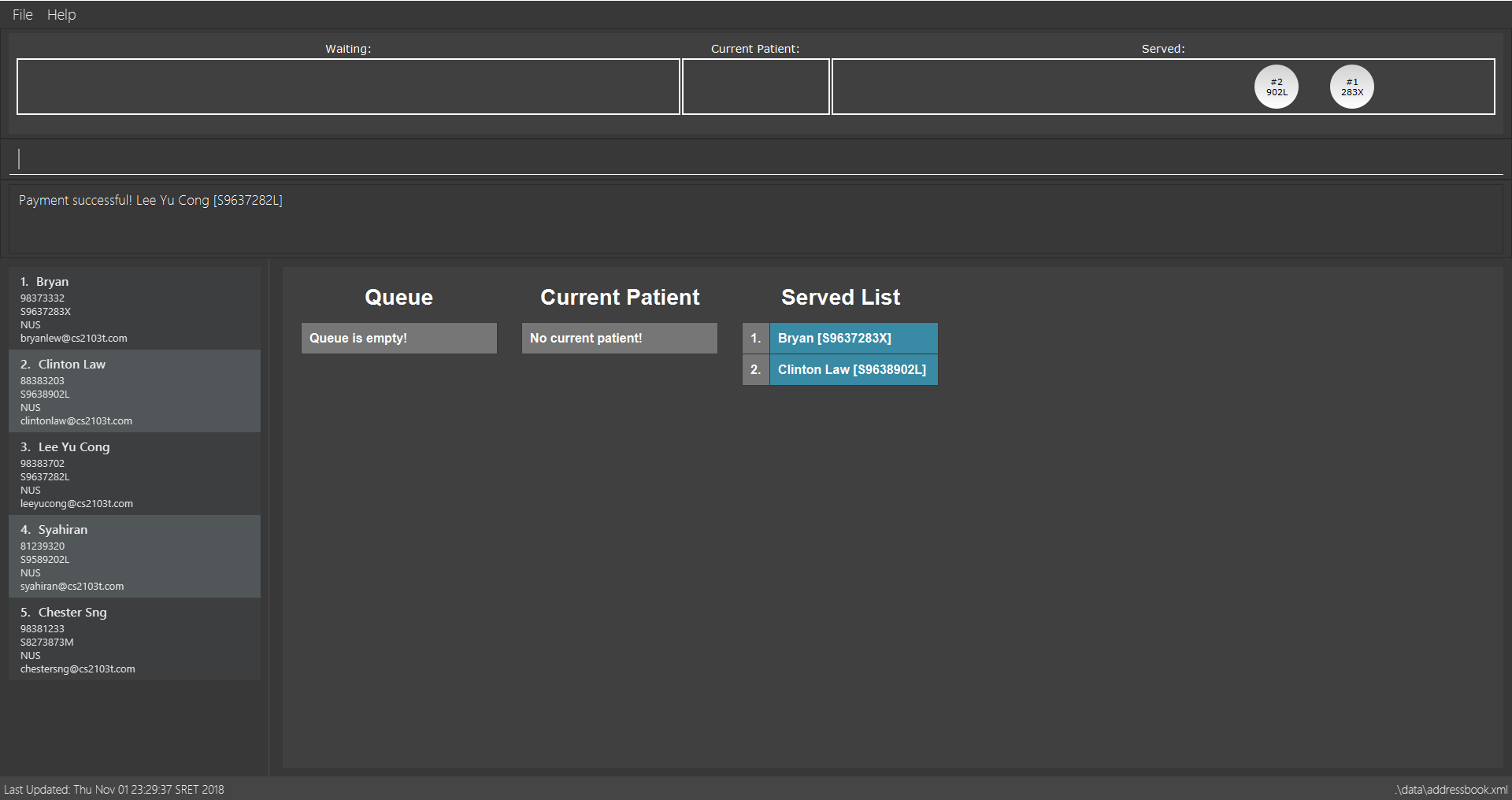
payment 3 command-
pay 1
Removes the 1st patient from the Served Patient Queue.
3.4. Document Generation
3.4.1. Generating medical certificate: mc
Does the patient need to be excused from school or work to rest? Let’s give him a medical certificate!
Format: mc INDEX
The patient’s INDEX in the Served Patient Queue must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
mc 1
Generates a medical certificate for the 1st patient in the Served Patient Queue.
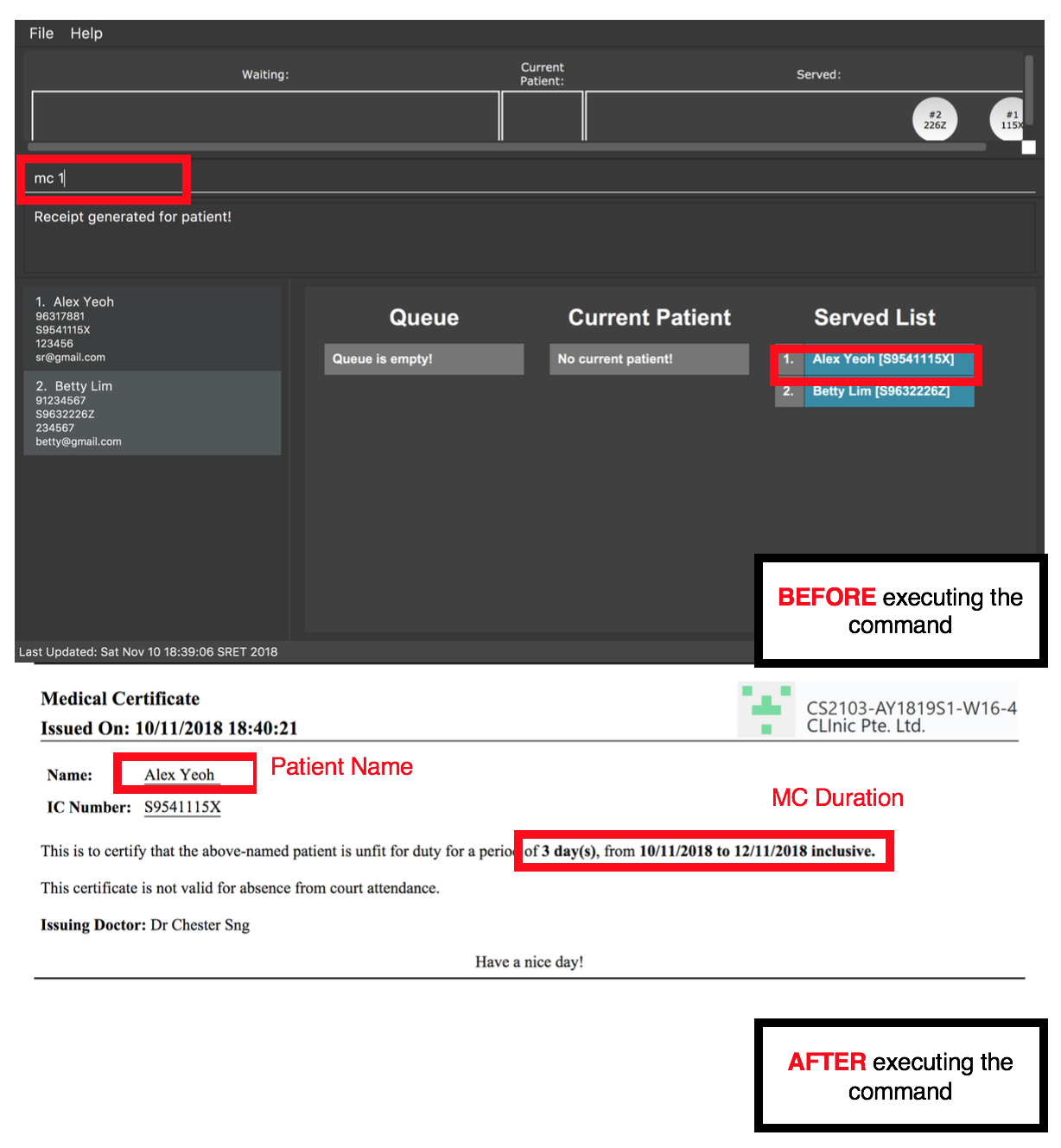
Alex Yeoh.3.4.2. Generating receipt: receipt
How much does today’s visit to the clinic cost? Let’s create a receipt for the patient!
Alias: rec
Format: receipt INDEX
The patient’s INDEX in the Served Patient Queue must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
receipt 5
Generates a receipt for the 5th patient in the Served Patient Queue.
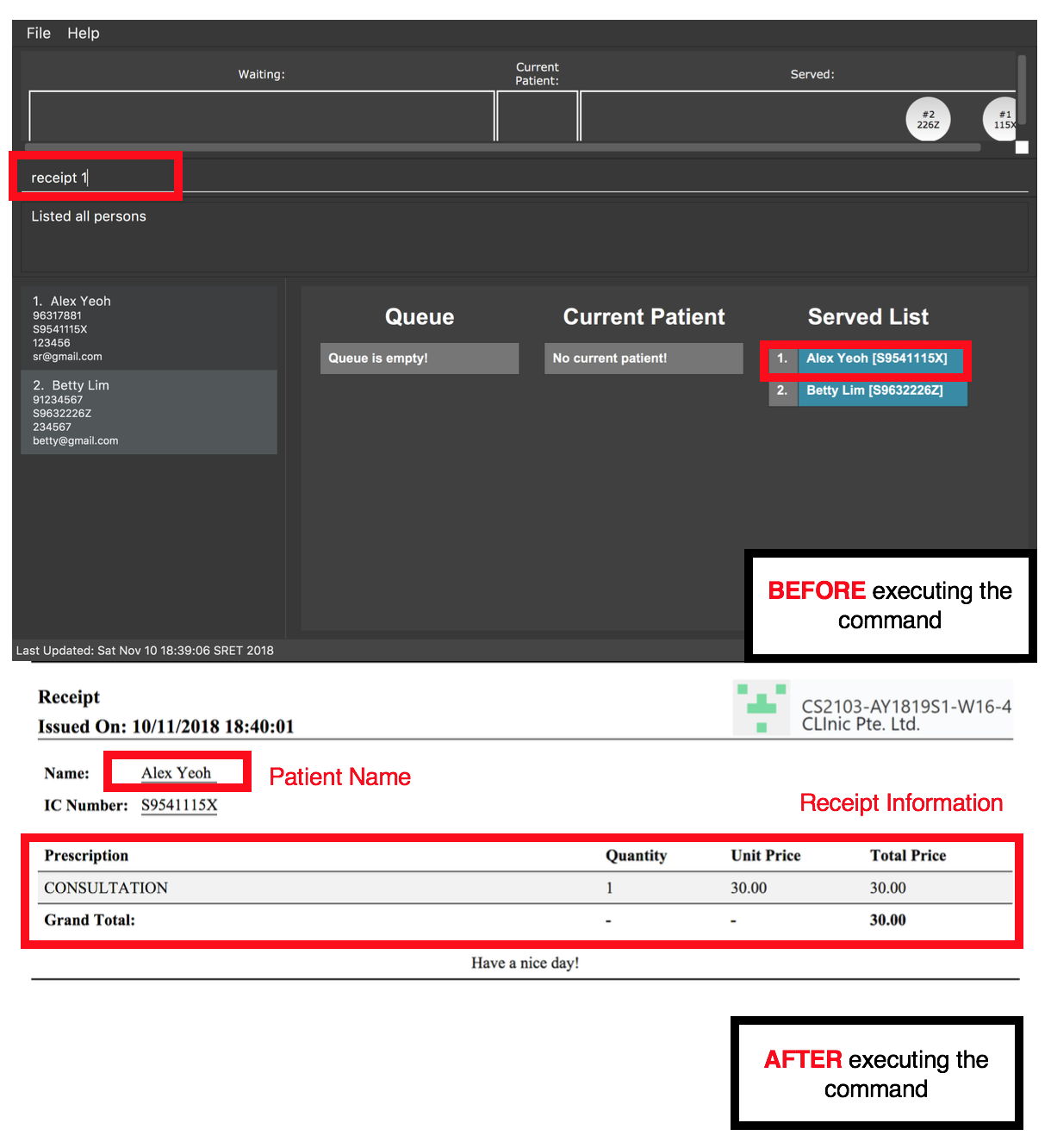
Alex Yeoh.3.4.3. Generating referral letter: refer
Does the patient need to consult a specialist? Let’s give him a referral letter!
Alias: ref
Format: refer INDEX
The patient’s INDEX in the Served Patient Queue must be a positive integer (i.e. 1, 2, 3, …).
|
Examples:
-
refer 7
Generates a referral letter for the 7th patient in the Served Patient Queue.
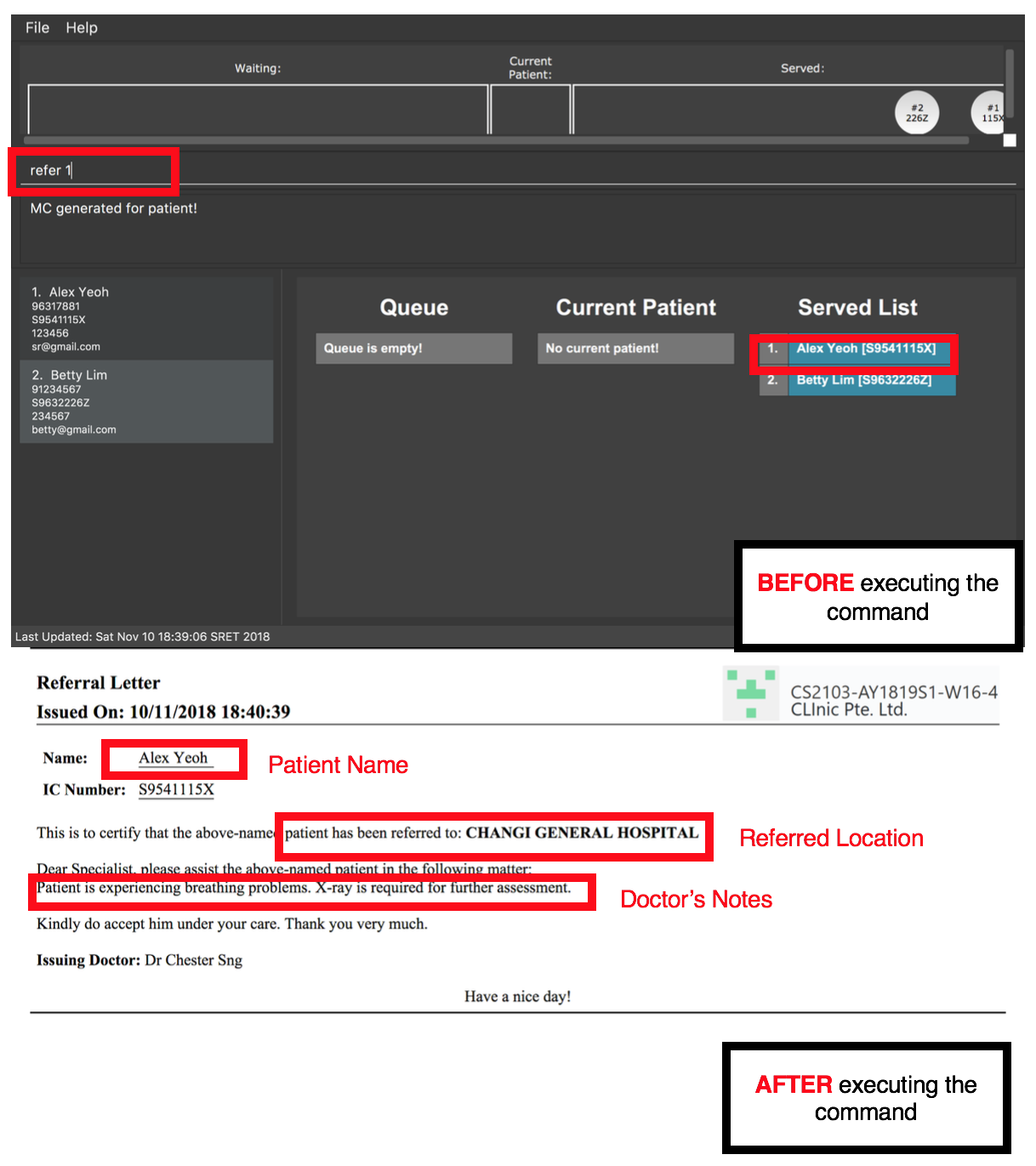
Alex Yeoh.3.5. Miscellaneous
3.5.1. Viewing help: help
Format: help
3.5.2. Listing entered commands: history
Lists all the commands entered, starting from the most recent to the oldest.
Alias: h
Format: history
|
Pro tip(s):
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box.
|
3.5.3. Undoing previous command: undo
Restores the address book to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Alias: u
Format: undo
|
Thing(s) to note:
Undoable commands: those commands that modify the database’s content ( |
Examples:
-
delete 1
list
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
select 1
list
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
addmedicine mn/panadol msq/100 ppu/5 sn/00000001 s/2500
undo(reverses theaddmedicinecommand)
3.5.4. Redoing the previously undone command: redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Alias: r
Format: redo
Examples:
-
delete 1
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command) -
delete 1
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies theclearcommand)
3.5.5. Exiting the program: exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
3.5.6. Saving the data
CLInic data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the application in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous CLInic folder.
Q: Why can’t I execute the finish command even if there is a Current Patient?
A: You are required to add notes to the Current Patient before using the finish command, use the adddocument command to add notes.
5. Command Summary
5.1. Patient
| Command Word | Command Alias | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
add |
|
|
|
list |
|
|
|
edit |
|
|
|
find |
|
|
|
delete |
|
|
|
select |
|
|
|
addmedicalrecord |
|
|
|
5.2. Medicine
| Command Word | Command Alias | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
addmedicine |
|
|
|
editmedicine |
|
|
|
restock |
|
|
|
liststock |
|
|
|
findmedicine |
|
|
|
checkstock |
|
|
|
5.3. Queue Management
| Command Word | Command Alias | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
register |
|
|
|
queue |
|
|
|
remove |
|
|
|
insert |
|
|
|
serve |
|
|
|
adddocument |
|
|
|
displaydocuments |
|
|
|
dispensemedicine |
|
|
|
finish |
- |
|
|
payment |
|
|
|
5.4. Document Generation
| Command Word | Command Alias | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
mc |
- |
|
|
receipt |
|
|
|
refer |
|
|
|
5.5. Miscellaneous
| Command Word | Command Alias | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
help |
- |
|
|
history |
|
|
|
undo |
|
|
|
redo |
|
|
|
exit |
- |
|
|